Categories
Archives
The latest update to IPTC NewsCodes, the 2024-Q1 release, was published on Thursday 28th March.
This release includes many updates to our Media Topic subject vocabulary, plus changes to Content Production Party Role, Horse Position, Tournament Phase, Soccer Position, Genre, User Action Type and Why Present.
UPDATE on 11 April: we released a small update to the Media Topics, including Norwegian (no-NB and no-NN) translations of the newly added terms, thanks to Norwegian news agency NTB.
We also made one label change in German: medtop:20000257 from “Alternative-Energie” to “Erneuerbare Energie,” This change was made at the request of German news agency dpa.
Changes to Media Topics vocabulary
As part of the regular review undertaken by the NewsCodes Working Group, many changes were made to the economy, business and finance branch of Media Topics. In addition, a number of changes were made to the conflict, war and peace branch in response to suggestions made by new IPTC member ABC Australia.
5 new concepts: sustainability, profit sharing, corporate bond, war victims, missing in action.
12 retired concepts: justice, restructuring and recapitalisation, bonds, budgets and budgeting, consumers, consumer issue, credit and debt, economic indicator, government aid, investments, prices, soft commodities market.
55 modified concepts: peacekeeping force, genocide, disarmament, prisoners of war, war crime, judge, economy, economic trends and indicators, business enterprise, central bank, consumer confidence, currency, deflation, economic growth, gross domestic product, industrial production, inventories, productivity, economic organisation, emerging market, employment statistics, exporting, government debt, importing, inflation, interest rates, international economic institution, international trade, trade agreements, balance of trade, trade dispute, trade policy, monetary policy, mortgages, mutual funds, recession, tariff, market and exchange, commodities market, energy market, debt market, foreign exchange market, loan market, loans and lending, study of law, disabilities, mountaineering, sport shooting, sport organisation, recreational hiking and climbing, start-up and entrepreneurial business, sharing economy, small and medium enterprise, sports officiating, bmx freestyle.
48 concepts with modified names/labels: judge, emergency incident, transport incident, air and space incident, maritime incident, railway incident, road incident, restructuring and recapitalisation, economic trends and indicators, exporting, importing, interest rates, balance of trade, mortgages, commodities market, soft commodities market, loans and lending, study of law, disabilities, mountain climbing, mountaineering, sport shooting, sport organisation, recreational hiking and climbing, start-up and entrepreneurial business, sports officiating, bmx freestyle, tsunami, healthcare industry, developmental disorder, depression, anxiety and stress, public health, pregnancy and childbirth, fraternal and community group, cyber warfare, public transport, taxi and ride-hailing, shared transport, business reporting and performance business restructuring commercial real estate residential real estate podcast, financial service, business service, news industry, diversity, equity and inclusion.
57 modified definitions: war crime, economy, economic trends and indicators, business enterprise, central bank, consumer confidence, currency, deflation, economic growth, economic organisation, emerging market, employment statistics, exporting, government debt, importing, inflation, interest rates, international economic institution, trade agreements, trade dispute, trade policy, mortgages, recession, tariff, market and exchange, commodities market, energy market, soft commodities market, debt market, foreign exchange market, loan market, loans and lending, disabilities, mountaineering, sport organisation, start-up and entrepreneurial business, sharing economy, small and medium enterprise, tsunami, healthcare industry, developmental disorder, depression, anxiety and stress, public health, pregnancy and childbirth, cyber warfare, public transport, taxi and ride-hailing, shared transport, business reporting and performance, business restructuring, commercial real estate, residential real estate, podcast, financial service, business service, news industry.
22 modified broader terms (hierarchy moves): peacekeeping force, genocide, disarmament, prisoners of war, business enterprise, central bank, consumer confidence, currency, gross domestic product, industrial production, inventories, productivity, economic organisation, emerging market, interest rates, international economic institution, international trade, monetary policy, mutual funds, tariff, loans and lending, bmx freestyle.
These changes are already available in the en-GB, en-US and Swedish (se) language variants. Thanks go to TT and Bonnier News for their work on the Swedish translation.
If you would like to contribute or update a translation to your language, please contact us.
Sports-related NewsCodes updates
We also made some changes to our sports NewsCodes vocabularies, which are mostly used by SportsML and IPTC Sport Schema.
New vocabulary: Horse Position
New entries in Tournament Phase vocabulary: Heat, Round of 16
New entry in Soccer Position: manager,
News-related NewsCodes updates
Content Production Party Role: new term Generative AI Prompt Writer which can also be used in Photo Metadata Contributor to declare who wrote the prompt that was used to generate an image.
Genre: new term User-Generated Content.
Why Present: new term associated.
The User Action Type vocabulary, mostly used by NewsML-G2, has had some major changes.
Previously this vocabulary defined terms related to specific social media services or interactions. We have retired/deprecated all site-specific terms (Facebook Likes, Google’s +1, Twitter re-tweets, Twitter tweets).
Instead, we have defined some generic terms: Like, Share, Comment. The pageviews term has been broadened into simply views (although the ID remains as “pageviews” for backwards-compatibility)
Thanks to the NewsCodes Working Group for their work on this release, and to all members and non-members who have suggested changes.
The IPTC News Architecture Working Group is happy to announce that the NewsML-G2 Guidelines and NewsML-G2 Specification documents have been updated to align with version 2.33 of NewsML-G2, which was approved in October 2023.
The changes include:
Specification changes:
- Adding the newest additions authoritystatus and digitalsourcetype added in NewsML-G2 versions 2.32 and 2.33
- Clarification on how @uri, @qcode and @literal attributes should be treated throughout
- Clarification on how roles should be added to infosource element when an entity plays more than one role
- Clarifying and improving cross-references and links throughout the document
Guidelines changes:
- Documentation of the Authority Status attrribute and its related vocabulary, added in version 2.32
- Documentation of the Digital Source Type element and its related vocabulary, added in version 2.33
- Clarification on how @uri, @qcode and @literal attributes should be treated throughout
- Clarifying and improving cross-references and links throughout the document
- Improved the additional resources section including links to related IPTC standards and added links to the SportsML-G2 Guidelines
- See the What’s New in NewsML-G2 2.32 and 2.33 section for full details.
We always welcome feedback on our specification and guideline documents: please use the Contact Us form to ask for clarifications or suggest changes.
 The IPTC is happy to announce the latest version of our guidance for mapping between photo metadata standards.
The IPTC is happy to announce the latest version of our guidance for mapping between photo metadata standards.
Following our publication of IPTC’s rules for mapping photo metadata between IPTC, Exif and schema.org standards in 2022, the IPTC Photo Metadata Working Group has been monitoring updates in the photo metadata world.
In particular, the IPTC gave support and advice to CIPA while it was working on Exif 3.0 and we have updated our mapping rules to work with the latest changes to Exif expressed in Exif 3.0.
As well as guidelines for individual properties between IPTC Photo Metadata Standard (in both the older IIM form and the newer XMP embedding format), Exif and schema.org, we have included some notes on particular considerations for mapping contributor, copyright notice, dates and IDs.
The IPTC encourages all developers who previously consulted the out-of-date Metadata Working Group guidelines (which haven’t been updated since 2008 and are no longer published) to use this guide instead.
We at IPTC receive many requests for help and advice regarding editing embedded photo and video metadata, and this has only increased with the recent news about the IPTC Digital Source Type property being used to identify content created by a generative AI engine.
In response, we have created some guidance: Developers’ and power users’ guide to reading and writing IPTC Photo Metadata
This takes the form of a wiki, so that it can be easily maintained and extended with more information and examples.
In its initial form, the documentation focuses on:
- Using the ExifTool command-line tool to read and write IPTC Photo Metadata,. ExifTool is commonly used by developers and power users to explore embedded metadata;
- Reading and writing image metadata in Python using the pyexiftool module;
- Reading and writing metadata in JavaScript (or TypeScript) using the node-exiftool module.
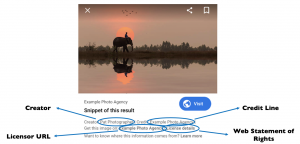
In each guide, we advise on how to read and create DigitalSourceType metadata for generative AI images, and also how to read and write the Creator, Credit Line, Web Statement of Rights and Licensor information that is currently used by Google image search to expose copyright information alongside search results.
We hope that these guides will help to demystify image metadata and encourage more developers to include more metadata in their image editing and publishing workflows.
We will add more guidance over the coming months in more programming languages, libraries and frameworks. Of particular interest are guides to reading and writing IPTC Photo Metadata in PHP, C and Rust.
Contributions and feedback are welcome. Please contact us if you are interested in contributing.
The IPTC is proud to announce that after intense work by most of its Working Groups, we have published version 1.0 of our guidelines document: Expressing Trust and Credibility Information in IPTC Standards.
The culmination of a large amount of work over the past several years across many of IPTC’s Working Groups, the document represents a guide for news providers as to how to express signals of trust known as “Trust Indicators” into their content.
Trust Indicators are ways that news organisations can signal to their readers and viewers that they should be considered as trustworthy publishers of news content. For example, one Trust Indicator is a news outlet’s corrections policy. If the news outlet provides (and follows) a clear guideline regarding when and how it updates its news content.
The IPTC guideline does not define these trust indicators: they were taken from existing work by other groups, mainly the Journalism Trust Initiative (an initiative from Reporters Sans Frontières / Reporters Without Borders) and The Trust Project (a non-profit founded by Sally Lehrman of UC Santa Cruz).
The first part of the guideline document shows how trust indicators created by these standards can be embedded into IPTC-formatted news content, using IPTC’s NewsML-G2 and ninjs standards which are both widely used for storing and distributing news content.
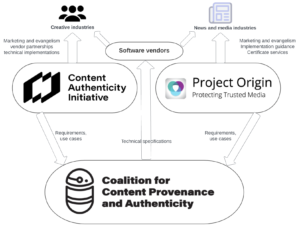
The second part of the IPTC guidelines document describes how cryptographically verifiable metadata can be added to media content. This metadata may express trust indicators but also more traditional metadata such as copyright, licensing, description and accessibility information. This can be achieved using the C2PA specification, which implements the requirements of the news industry via Project Origin and of the wider creative industry via the Content Authenticity Initiative. The IPTC guidelines show how both IPTC Photo Metadata and IPTC Video Metadata Hub metadata can be included in a cryptographically signed “assertion”
We expect these guidelines to evolve as trust and credibility standards and specifications change, particularly in light of recent developments in signalling content created by generative AI engines. We welcome feedback and will be happy to make changes and clarifications based on recommendations.
The IPTC sends its thanks to all IPTC Working Groups that were involved in creating the guidelines, and to all organisations who created the trust indicators and the frameworks upon which this work is based.
Feedback can be shared using the IPTC Contact Us form.
The IPTC NewsCodes Working Group has approved an addition to the Digital Source Type NewsCodes vocabulary.

The new term, “Composite with Trained Algorithmic Media“, is intended to handle situations where the “synthetic composite” term is not specific enough, for example a composite that is specifically made using an AI engine’s “inpainting” or “outpainting” operations.
The full Digital Source Type vocabulary can be accessed from https://cv.iptc.org/newscodes/digitalsourcetype. It can be downloaded in NewsML-G2 (XML), SKOS (RDF/XML, Turtle or JSON-LD) to be integrated into content management and digital asset management systems.
The new term can be used immediately with any tool or standard that supports IPTC’s Digital Source Type vocabulary, including the C2PA specification, the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard and IPTC Video Metadata Hub.
Information on the new term will soon be added to IPTC’s Guidance on using Digital Source Type in the IPTC Photo Metadata User Guide.
NEW YORK, NY, 26 JULY 2023: The IPTC today announced the beginning of a public feedback and review period of IPTC Sport Schema, which aims to be “the standard for the next generation of sports data.”
The announcement was made by Paul Kelly, Lead of the IPTC Sports Content Working Group, at the Sports Video Group’s Content Management Forum held at 230 Fifth Penthouse, New York.
“The SVG Content Management Forum is attended by senior tech experts from sports broadcasters and sports leagues from the US and around the world, so it is the perfect place to launch the IPTC Sport Schema,” said Kelly. “Many members of SVG have advised us on our work so far, including organisations such as Warner Bros Discovery, NBC Universal, PGA TOUR, Major League Baseball and Riot Games. Presenting our work at their event is a great way to say thanks for their help.”
While not yet an official IPTC standard, the IPTC Sports Content Working Group feels that the schema describing IPTC Sport Schema is solid enough to be published for public feedback.
Sports data for the era of linked data and knowledge graphs
The purpose of the IPTC Sport Schema project is to create a new RDF-based sports data standard, while making the most of the experience the IPTC has gained from the last 20 years of maintaining SportsML, the open XML-based sports data standard used by news and sports organisations around the world.
While XML served the industry well for many years, more recently developers and IPTC members have asked the Sports Content Working Group whether a standard would become available in a more modern serialisation format such as JSON, and whether knowledge graph protocols would be supported.
Because it is based on the W3C-standard RDF and OWL specifications, IPTC Sport Schema leverages the wide range of tools and expertise in the world of knowledge graphs, semantic web and linked open data, including the SPARQL query language, the JSON-LD serialisation into JSON format, inference using RDF Schema and OWL, and more.
“Using IPTC Sport Schema, sports leagues can choose to own their data,” said IPTC Managing Director Brendan Quinn. “Content publishers or sports leagues can publish open data on their website if they choose, in a way that can be re-mixed and re-used by others around the world.” IPTC Sport Schema can also be used for a more traditional model of aggregation and syndication by sports statistics providers who add value to the raw data being collected by sports leagues.
Like its ancestor SportsML, IPTC Sport Schema is created as a generic sports data model that can represent results, statistics, schedules and rosters across many sports. “Plugins” for specific sports extend the generic schema with specific statistics elements for 10 sports such as soccer, motor racing, tennis, rugby and esports. But the generic model can be used to handle any competitive sports competition, either team-based, head-to-head or individual.
As well as IPTC’s SportsML standard, the project is based on previous work by the BBC on its BBC Sport Ontology (some of its creators worked on this project). We have also consulted with and analysed related projects and formats such as OpenTrack and the IOC’s Olympics Data Feed format.
For more information on IPTC Sport Schema, please see the dedicated site sportschema.org, the project’s GitHub repository,
Those who are interested in the details can see an introduction to the IPTC Sport Schema ontology design, the full ontology diagram or full RDF/OWL ontology documentation,
There may be significant changes to the schema between now and when it is released as a fully endorsed IPTC Standard, so we don’t recommend that it is implemented in production systems yet. But we welcome analysis and experimentation with the model, and look forward to seeing feedback from those who would like to implement it in the real world.
People and organisations who are not IPTC members can give feedback by posting to the IPTC SportsML public discussion group or use the IPTC Contact Us form.

Following the recent announcements of Google’s signalling of generative AI content and Midjourney and Shutterstock the day after, Microsoft has now announced that it will also be signalling the provenance of content created by Microsoft’s generative AI tools such as Bing Image Creator.
Microsoft’s efforts go one step beyond those of Google and Midjourney, because they are adding the image metadata in a way that can be verified using digital certificates. This means that not only is the signal added to the image metadata, but verifiable information is added on who added the metadata and when.
As TechCrunch puts it, “Using cryptographic methods, the capabilities, scheduled to roll out in the coming months, will mark and sign AI-generated content with metadata about the origin of the image or video.”
The system uses the specification created by the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity. a joint project of Project Origin and the Content Authenticity Initiative.
The 1.3 version of the C2PA Specification specifies how a C2PA Action can be used to signal provenance of Generative AI content. This uses the IPTC DigitalSourceType vocabulary – the same vocabulary used by the Google and Midjourney implementations.
This follows IPTC’s guidance on how to use the DigitalSourceType property, published earlier this month.

As a follow-up to yesterday’s news on Google using IPTC metadata to mark AI-generated content we are happy to announce that generative AI tools from Midjourney and Shutterstock will both be adopting the same guidelines.
According to a post on Google’s blog, Midjourney and Shutterstock will be using the same mechanism as Google – that is, using the IPTC “Digital Source Type” property to embed a marker that the content was created by a generative AI tool. Google will be detecting this metadata and using it to show a signal in search results that the content has been AI-generated.
A step towards implementing responsible practices for AI
We at IPTC are very excited to see this concrete implementation of our guidance on metadata for synthetic media.
We also see it as a real-world implementation of the guidelines on Responsible Practices for Synthetic Media from the Partnership on AI, and of the AI Ethical Guidelines for the Re-Use and Production of Visual Content from CEPIC, the alliance of European picture agencies. Both of these best practice guidelines emphasise the need for transparency in declaring content that was created using AI tools.
The phrase from the CEPIC transparency guidelines is “Inform users that the media or content is synthetic, through
labelling or cryptographic means, when the media created includes synthetic elements.”
The equivalent recommendation from the Partnership on AI guidelines is called indirect disclosure:
“Indirect disclosure is embedded and includes, but is not limited to, applying cryptographic provenance to synthetic outputs (such as the C2PA standard), applying traceable elements to training data and outputs, synthetic media file metadata, synthetic media pixel composition, and single-frame disclosure statements in videos”
Here is a simple, concrete way of implementing these disclosure / transparency guidelines using existing metadata standards.
Moving towards a provenance ecosystem
IPTC is also involved in efforts to embed transparency and provenance metadata in a way that can be protected using cryptography: C2PA, the Content Authenticity Initiative, and Project Origin.
C2PA provides a way of declaring the same “Digital Source Type” information in a more robust way, that can provide mechanisms to retrieve metadata even after the image was manipulated or after the metadata was stripped from the file.
However implementing C2PA technology is more complicated, and involves obtaining and managing digital certificates, among other things. Also C2PA technology has not been implemented by platforms or search engines on the display side.
In the short term, AI content creation systems can use this simple mechanism to add disclosure information to their content.
The IPTC is happy to help any other parties to implement these metadata signals: please contact IPTC via the Contact Us form.
At today’s Google I/O event keynote, Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google, explained how Google will be using embedded IPTC image metadata to signal visual media created by generative AI models.
“Moving forward, we are building our models to include watermarking and other techniques from the start,” Pichai said. “If you look at a synthetic image, it’s impressive how real it looks, so you can imagine how important this is going to be in the future.
“Metadata allows content creators to associate additional context with original files, giving you more information whenever you encounter an image. We’ll ensure every one of our AI-generated images has that metadata.”
The IPTC Photo Metadata section of Google Images’ guidance on metadata has been updated with new guidance on the DigitalSourceType field:
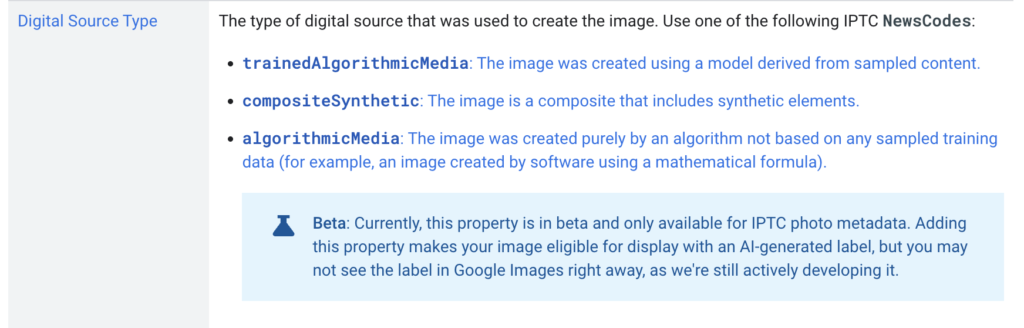
This follows the guidance on IPTC Photo Metadata for Generative AI that was recently published by IPTC.
“AI-Generated” label on Google Images
The above guidance hints at an “AI-generated label” to be used on Google Images in the future. Google recommends that all creators of AI-generated images use the IPTC Digital Source Type property to signal AI-generated content. While Google says that “you may not see the label in Google Images right away”, it appears that it will soon be available in Google Images search results.