Categories
Archives
Our current Managing Director Michael Steidl is retiring in the summer of 2018 after 15 years of dedicated service to the IPTC. The IPTC is now seeking applicants to be the next Managing Director of our organization. Feel free to contact Michael (office@iptc.org) or our Chair, Stuart Myles, (chair@iptc.org) if you have any questions.
Job Opportunity: Managing Director of IPTC
For more information about the position, read the full Managing Director profile.
The IPTC is seeking applications for the next Managing Director of our organization. We are the global standards body of the news media and provide the technical foundation for the news ecosystem. Our mission is to simplify the distribution of information. We develop and promote efficient technical standards to improve the management and exchange of information between content providers, intermediaries and consumers.
The Managing Director, working with the Board and Membership, seeks to broaden adoption of IPTC standards, to maximize information sharing between members and to collaborate with partners across the news and media industry. The ideal applicant will have a strong record of working with news technology, presenting a positive image of an organization and administering a membership or non profit organization.
Learn more about IPTC and read the full Managing Director profile.
Applicants should email a letter of interest, curriculum vitae and contact information for three references to office@iptc.org. We will start considering applications on 1 December 2017.
A ODRL (Open Rights Digital Language) Candidate Recommendation was released by W3C’s Permissions & Obligations Expressions (POE) Working Group on 26 September: ODRL has been updated to a generic information model that can be customized by any industry or business sector. IPTC is looking for members and experts with experience in defining licensing information in a machine-readable way to help adapt IPTC’s RightsML standard according to the new ODRL Recommendation, which will specifically address the needs of the news industry.
IPTC’s RightsML – https://iptc.org/standards/rightsml/ – is a standard providing a data model for marking up rights expressions about content of all relevant media types in a machine-readable way. The standard was introduced in 2012 and from the start it was built on ODRL – Open Digital Rights Language – a rights expression framework defined outside IPTC. At that time, a W3C Community Group was backing ODRL.
In early 2016 W3C established a formal Permissions & Obligations Expressions (POE) Working Group – https://www.w3.org/2016/poe/charter – to make a W3C Recommendation from the Community Group specifications, and on 26 September a Candidate Recommendation was released. The work on that W3C Recommendation will be closed by the end of 2017, and IPTC will take action to align a next RightsML version with the Recommendation.
IPTC Action: Update RightsML by Synchronising It With the New W3C Recommendation as ODRL RightsML Profile
The transfer of ODRL from a Community Group to a Recommendation approved by the W3C Consortium was not only a copy and paste action. The basic design has not been changed but the status of many actions, constraints or party functions has been changed from “normative” to “non-normative.” The reason was to make the ODRL Recommendation a generic information model which can be easily adapted to the different needs of various business sectors. This has been demonstrated by the range of participants of the W3C Working Group covering needs and interests from media companies and their trade associations, financial data providers, and universities.
The solution for that is called ODRL Profile: it defines all the actions, kinds of constraints, types of involved parties and more which are typical to a business sector and these definitions are add-ons to the basic Information Model of the Recommendation. This also slims down the specifications: businesses behind media assets don’t have to take care of the requirements regarding e.g. scientific papers.
IPTC has taken the role of defining the RightsML Profile of ODRL covering the needs of the news industry. Writing down the definitions fitting into the context of ODRL will not be that hard. Michael Steidl and Stuart Myles of the IPTC are invited experts of the ODRL/POE Working Group and have been active in its development from the start.
The big challenge is to determine which business needs of the news industry should be covered by the actions, constraints or parties defined by the RightsML Profile. To achieve that we need people from IPTC members and experts from other companies who have any experience in defining licensing information in a machine-readable way. Regular conference calls will take place from October 2017 to early 2018 to select and define what should be included to update RightsML Profile.
ODRL: From Candidate Recommendation to the Final Recommendation
On 26 September 2017, W3C published the Candidate Recommendation of ODRL. Links to the relevant W3C documents and other relevant resources are provided in the Details section below.
This opens a test phase until mid-November; in this period the Information Model and Vocabulary documents should be reviewed and comments may be posted. Further, W3C procedures specify that the Information Model and Vocabulary should be implemented into software at least by two parties and be tested against a list of criteria. Any party interested in ODRL and all IPTC members are invited to take this action. For more information contact Michael Steidl (mdirector@iptc.org).
Details for Creating the RightsML ODRL Profile:
- POE Working Group Charter: https://www.w3.org/2016/poe/charter
- POE Working Group home page: https://www.w3.org/2016/poe/wiki/Main_Page
- ODRL Information Model – Candidate Recommendation: https://www.w3.org/TR/2017/CR-odrl-model-20170926/
- ODRL Vocabulary – Candidate Recommendation: https://www.w3.org/TR/2017/CR-odrl-vocab-20170926/
- RightsML Profile outline: http://w3c.github.io/poe/rightsml/ (currently only the section heads are shown)
- The RightsML landing page of the IPTC website: https://iptc.org/standards/rightsml/
- The current RightsML on the IPTC Developer Site: http://dev.iptc.org/RightsML
- The current and small RightsML specification document: http://www.iptc.org/std/RightsML/1.1/RightsML_1.1EP2-spec_1.pdf
- IPTC contact: Michael Steidl – mdirector@iptc.org
IPTC’s Board of directors and Michael Steidl jointly announce that Michael will retire from employed work in mid-2018 and he will step down as IPTC’s Managing Director by then.
The Board has already started to make plans for selecting a new IPTC Managing Director and will provide more details in a separate communication.
Stuart Myles
Chairman of the IPTC Board
Being IPTC’s Managing Director for 15 years is a great experience and I’m happy about having been involved in the development and roll-out of 9 new standards, the new Media Topic taxonomy and other vocabularies; further in setting up new formats of the face -to-face meetings and in the creation of new types of meetings. Being in contact with our membership is also part of the bright side of my IPTC life and I enjoyed spreading the word about IPTC and its work among people knowing only little or nothing about our organisation. It was great to welcome 74 new members in this period.
Unfortunately, even such a great period of life started to apply burden on me, so I’ve decided to retire from employed work next summer. Please look forward to what the future will bring.
Michael Steidl
Managing Director of IPTC
IPTC named Bill Kasdorf, longtime publishing executive and VP and Principal Consultant at Apex Content and Media Solutions, as its new Public Relations Chairperson.
IPTC is a consortium of news agencies, publishers and industry vendors that develops and publishes technical specifications and standards to promote the easy, accurate and inexpensive sharing of news and information in all media. Kasdorf’s main goals as Marketing and Public Relations Chairperson are to increase and strengthen the membership of IPTC, and to extend awareness of IPTC’s work to other sectors of publishing beyond news that would benefit from IPTC’s work.
“Although the technical standards developed by IPTC are rooted in the news media sector, the work of IPTC is incredibly important and useful to all areas of publishing and media, as well as related fields such as library science and the cultural heritage sector,” Kasdorf said.
Kasdorf’s experience gives him a broad perspective across the major sectors of the publishing ecosystem – trade books, educational publishing, scholarly and scientific books and journals, magazines, and news. General editor of The Columbia Guide to Digital Publishing, he is active in many professional and standards organizations. He serves on the Steering Committee of the W3C Publishing Business Group and is a member of the W3C Publishing Working Group; he chairs the Content Structure Committee of the Book Industry Study Group; and he is active in the Society for Scholarly Publishing, of which he is a Past President. He serves on the editorial boards of Learned Publishing and the Journal of Electronic Publishing.
In his consulting practice, Kasdorf has served clients globally, including large international publishers such as Pearson, Wolters Kluwer, and Kaplan; scholarly presses such as Harvard, MIT, and Cambridge; aggregators such as VitalSource; and global organizations such as the World Bank, the British Library, and the European Union.
“The PR Chairperson should combine ideas from our membership with needs from up-to-date marketing strategies and Bill will do this in an excellent way” said Michael Steidl, Managing Director of IPTC.
“IPTC is at the forefront of the publishing ecosystem in the development and implementation of machine processable rights expressions, as well as photo and video metadata,” Kasdorf said. “We live in a multimedia world, and IPTC is providing essential technologies for making that world work.”
After 12 years of collaborative work on establishing and implementing photo metadata standards, IPTC, the global technical standards body of the news media and related industries, announced Adobe Systems Incorporated is joining as a Voting Member. Adobe’s membership was announced at IPTC’s Spring Meeting today in London.
“Adobe is a key player in the media production ecosystem, so we are thrilled to welcome them as a member of the IPTC,” said Stuart Myles, Chairman of the Board of IPTC, and Director of Information Management at Associated Press. “We look forward to working together with Adobe on driving continued improvements in the workflows of photo and video creators around the world.”
“Adobe has a long history of working informally with the IPTC, and we look forward to further success as we participate directly and contribute as a Voting Member,” said Dr. Scott Foshee, Principal Scientist, Adobe. “Our close involvement will not only enable greater coordination between Adobe and the IPTC, but will also allow Adobe to facilitate better coordination across the photography standardization community.”
Photo metadata is key to protecting images’ copyright and licensing information, and for managing digital assets. IPTC’s Photo Metadata Standard, created with contributions by Adobe, is the most widely used because of universal acceptance among photographers, distributors, news organisations, archivists, and developers. Adobe’s metadata management software, which supports the IPTC standard, is used by Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, Illustrator, Acrobat, and Premiere.
“Adobe’s implementation has made IPTC photo metadata very popular,” added Michael Steidl, IPTC Managing Director. “For 12 years we have been collaborating on fostering professional use of IPTC photo metadata by photo businesses – building on our success by conducting research and incorporating feedback from users. This membership will open yet more opportunities for better tagging of photos and videos.”
Adobe first adopted IPTC IIM metadata in Photoshop around 1994 and later created the metadata format XMP. In 2004 IPTC and Adobe joined forces to support a consistent use of metadata: The first IPTC Photo Metadata Standard was created jointly. A main goal of the standard was to provide support for photographers and photo editors to use the fields in correct and consistent ways.
Adobe will be a Voting Member of IPTC, signifying Adobe as a key player and industry leader. IPTC currently has about 60 members. Its voting members take part in all decisions regarding IPTC standards. Delegates can participate in working parties and groups, may request changes, and make contributions to standards’ development.
News Classification Rules Being Developed for English and German with IPTC Media Topics
The IPTC has reached the first milestone in EXTRA, the Google/DNI project to build an open source rules engine for news. We are partnering with Infalia PC and have selected the Elasticsearch engine for developing a high-performance, rules-based news classifier. We are licensing an English language news corpus from Reuters and one in German from the Austrian Press Agency for use within the project. We have two linguists creating sample rules for classifying those corpora with IPTC’s Media Topics using the EXTRA engine. The project is on track to deliver a working version of the engine, together with the sample rules, by the summer of 2017.
EXTRA Open Source Rules for News
EXTRA (“EXTraction Rules Apparatus”) is an open source project to classify news text using rules. The engine allows news organizations to precisely identify the categories to which a piece of news belongs by specifying Boolean rules, with sophisticated natural language processing capabilities. Rule-based classification is better for breaking news than statistical methods, since it doesn’t require re-training using example news items (which typically take time to produce). Automated classification is generally more consistent and scalable than hand tagging of news. Most machine learning techniques are essentially “black boxes”, whereas rules provide much greater transparency – and therefore ability to control – why a piece of content is classified in a particular way. For all of these reasons, we believe that the EXTRA rules engine is ideally suited for news classification.
Elasticsearch Percolator
After evaluating a number of open source frameworks, we decided to make Elasticsearch’s percolator technology the foundation for the EXTRA engine. Our testing indicates that Elasticsearch supports indexing a large number of rules. The percolator has performant and scalable support for matching indexed rules against incoming documents, the core task of the EXTRA engine. Elasticsearch has an active open source community, as well as options for commercial support.
The EXTRA Requirements, Design, API and Rules Language
We have drawn up a detailed set of technical requirements and have created a high level technical architecture for EXTRA. We have designed the EXTRA API and the rule language. Linguists are working on writing the rules to classify English and German news using IPTC’s Media Topics taxonomy
IPTC, Infalia, Google DNI
EXTRA is being developed by the IPTC, an international consortium of news agencies, publishers and system vendors. The project is funded by the Digital News Initiative, Google’s €150 million fund aimed at stimulating innovation amongst European publishers. In 2016, IPTC applied for and won a DNI grant of €50,000 to develop the EXTRA engine. As a development partner, IPTC selected Infalia PC, a spin-out from the Information Technologies Institute of the Centre for Research and Technology Hellas with significant expertise in data analytics and natural language processing.
If you’d like to learn more about the IPTC or the EXTRA project, please contact office@iptc.org
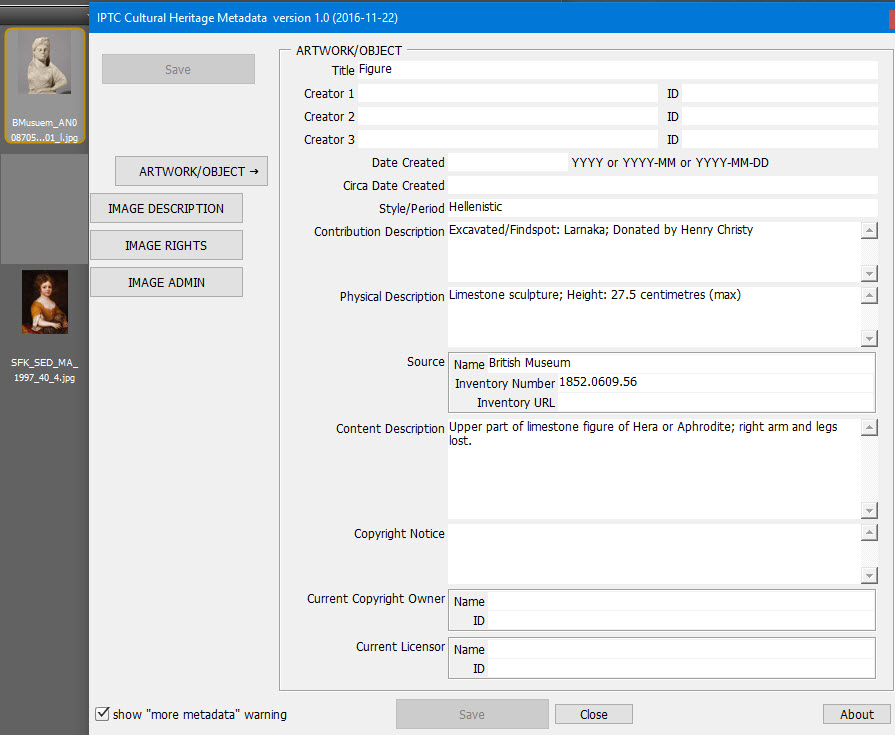
IPTC’s Photo Metadata Working Group has released the Cultural Heritage Panel plugin for Adobe Bridge, which focuses on fields relevant for images of artwork and other physical objects, such as artifacts, historical monuments, and books and manuscripts.
Sarah Saunders and Greg Reser, experts from the cultural heritage sector, conceived the IPTC Cultural Heritage Panel to address needs of the photo business and growing community of museums, art foundations, libraries, and archive organisations. Furthermore the panel fills a gap: Many imaging software products, including Bridge, do not support all metadata fields of the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard 2016 for artwork or objects.
The artwork or object fields – a special set of metadata fields developed by IPTC a few years ago – describe artworks and objects portrayed in the image (for example, a painting by Leonardo da Vinci). This means that descriptive and rights information about artworks or objects is recorded separately from information about the digital image in which they are shown. Multiple layers of rights and attribution can be expressed – copyright in the photo may be owned by a photographer or museum, while the copyright in the painting is owned by an artist or estate.
The new plugin for Bridge (CC versions up to 2016 and CS6 were tested) allows people to view the image data, and write into these fields using a simple panel, which has been tailor-made for use in the heritage sector. The panel includes fields for artwork/object attributes and also relevant digital image rights.
“The Cultural Heritage Panel will be very useful for people working in the heritage sector in museums and archives,” Saunders, a consultant specialising in digital imaging and archiving. “It allows them to manage and monitor data about objects and artworks that is embedded in the IPTC XMP fields in the image.”
The panel is especially helpful for small organisations without digital asset management systems, and large organisations with many individual contributors – all of whom may enter metadata into the standard fields using Adobe Bridge, said Reser, a metadata analyst for the University of California, San Diego, who wrote the JavaScript code for the project.
“The metadata can then be transferred into an organisation’s digital asset management system; the panel helps ease the ingest process,” Reser said.
Reser also noted that the panel helps incorporate more people into workflows, such as freelance photographers, who otherwise may not have access to an organisation’s digital asset management system. The Cultural Heritage Panel allows them to be an efficient part of the process of viewing the metadata included with an image, and adding to it when appropriate.
“IPTC is the most popular schema in embedded metadata,” Reser said. “Over time I bet we’ll see a lot of the cultural heritage fields creep into off-the-shelf programs and software.”
The panel is free, includes an easy-to-use interface, and includes key image administration fields. Image caption and keywords can be automatically generated from existing Artwork or Object data.
Download the IPTC Cultural Heritage Panel and User Guide for Adobe Bridge.
Questions? Contact us.
Twitter: @IPTC
LinkedIn: IPTC
The IPTC has released a comprehensive set of sports controlled vocabularies as a supplement to the SportsML 3.0 sports-data interchange format, which was released in July 2016. These controlled vocabularies (CVs) are in the format of NewsML-G2 NewsML-G2 Knowledge Items plus RDF variants and are available on IPTC’s CV server at http://cv.iptc.org/newscodes.

There are 113 CVs representing such core sports concerns such as event and player status, as well as specialized lists for 11 sports (basketball, soccer, rugby, American football, etc.) for statistics, player positions, scoring types, etc.
“The SportsML 3.0 standard’s semantic tech capabilities are improved greatly by the new controlled vocabularies,” said Trond Husø, system developer for Norwegian news agency NTB, one of the early adopters of SportsML 3.0. “Data can be easily imported, structured, and stored.”
“When building a sports app you spend a lot of prep time defining your terms and building a schema,” said Paul Kelly, news technology consultant and lead for IPTC’s Sports Content Working Group. “By using SportsML 3.0, there is no need to reinvent the wheel.”
“You consider things such as ‘What sort of results and stats do we need?’ and ‘How will our system handle interrupted matches?’ IPTC’s vocabularies can get you on your way because they properly define in a standard format almost all the terminology you would use in a sports application: Everything from “goals-scored” to a full enumeration of status codes for sports events,” Kelly said.
For the Summer 2016 Olympics, NTB acquired the rights to distribute the results and data from the International Olympics Committee’s Olympic Data Feed (ODF). NTB then transformed ODF to SportsML 3.0, and then to NITF3.2. “Using SportsML to structure the ODF’s data is a broad and comprehensive solution to approaching all sports and competitions worldwide,” said Husø, who is also a member of IPTC’s Sports Content Working Group. “SportsML is now a truly flexible and universal format that can incorporate multiple vendor codes and still provide a defense against vendor lock-in.”
“Terms defined in another format such as ODF can easily live beside SportsML terms – as well as any other proprietary format – so that an organisation can build a repository of knowledge of all the different sports-data formats,” Kelly said.
Another advantage to the new SportsML 3.0 standard is that if new concepts are added to a sports vocabulary or modified in it, the data model and the XML Schema don’t change; they stay stable. It also supports all languages for the concept labels.
“A great feature is that we can translate the definitions to Norwegian – without changing or breaking the vocabulary,” said Husø. “If we were to distribute internationally, our domestic receivers could look up the definitions in Norwegian, while the international ones could use the English term.”
IPTC’s SportsML 3.0 standard underwent a major upgrade from version 2.2, after 12 years of evolution since its first version. The new standard incorporates contribution from sports experts in 12 countries. Its flexible core covers all major sports and events in most news reporting.
Other early adopters of SportsML 3.0 include Univision and the British Press Association in its new multi-sport API. Its major features include:
- compliance with IPTC’s NewsML-G2 standard
- a flexible core that covers all major sports and events in most news reporting
- plugins for detailed stats in 10+ sports
- a more flexible tournament model
- schedules, scores, standing, statistics, etc.
- choices between specific and generic terms
- controlled vocabularies, semantic tech capabilities
- schema redesign
- many samples and tool support.
Tool support for SportsML 3.0 includes 45 samples from 11 different sports and events, including both classic and SportsML-G2 examples, and both generic and specific examples.
The vocabularies will be maintained by IPTC for future expansion; new sports and terms can be added.
For more information on SportsML 3.0:
SportsML 3.0 Standard, including Zip package
SportsML 3.0 Specification Documents
NewsML-G2 Standard
Contact: Trond Husø @trondhuso, Trond.Huso@ntb.no
IPTC has published an updated Photo Metadata User Guide, for photographers, photo editors and professionals responsible for in-house metadata workflows, including digital asset management (DAM) systems.
Based on IPTC’s widely used Photo Metadata Standard, the new User Guide contains practical information regarding photo metadata – from photographers familiarizing themselves with basics, to managers in related businesses who have a deeper understanding of implementation of standards and metadata.
A key use of metadata is to describe the content of an image, location and rights information; the guide groups metadata fields according to information types. “The User Guide will help when deciding where metadata should be put about a certain topic, and what data should or should not be filled into a specific field,” said Michael Steidl, managing director of IPTC, and lead of IPTC’s Photo Metadata Working Group.
IPTC sets the industry standard for administrative, descriptive, and copyright information about images. The IPTC Photo Metadata Standard, supported by many software applications, is the most widely used standard because of its universal acceptance among photographers, distributors, news organisations, archivists, and developers.
The Photo Metadata User Guide walks users through the major groups of metadata, and for each IPTC field contained within each, it provides short guidelines on the use and semantics.
The first section of the guide outlines practical use for a basic understanding of applying photo metadata, and may be most helpful to photographers becoming familiar with adding it to their photos for the first time. Photo metadata is key to protecting photographers’ images, including copyright and licensing information online.
The User Guide addresses typical questions such as:
- What is a minimum set of fields to be used?
- How is metadata preserved?
Five examples of metadata for independent, staff, and agency photographers plus images of artwork are given.
Photo metadata is also essential for managing digital assets. Detailed and accurate descriptions about images ensure they can be easily and efficiently retrieved via search, by users or machine-readable code. This results in smoother workflow within organisations, more precise tracking of images, and potential for licensing opportunities.
For professionals responsible for in-house photo metadata workflows and DAM systems, all IPTC metadata fields in the User Guide have been grouped by topic for easy reference: general description, persons, locations, things shown, rights and licensing information, and administrative data.
The User Guide does not focus on the user interface of a specific software, and will be updated regularly to include more details.
For questions about the Photo Metadata User Guide or about becoming involved in IPTC’s work: Contact us.
Twitter: @IPTC
LinkedIn: IPTC
IPTC is looking for software developers to design, develop, document and test EXTRA, an open source rules-based classification engine for news. First preference will be given to applications received by 21st October 2016, and review will continue until the positions are filled.
“Classification” means assigning one or more categories to the text of a news document. Rules-based classifiers use a set of Boolean rules, rather than machine-learning or statistical techniques, to determine which categories to apply.
EXTRA is the EXTraction Rules Apparatus, a multilingual open-source platform for rules-based classification of news content. IPTC was awarded a grant of €50,000 from the first round of Google’s Digital News Initiative Innovation Fund to build and freely distribute the initial version of EXTRA. DNI granted IPTC €50,000 for the entire project.
We are working with news providers to supply sets of news documents and with linguists to write rules to classify the documents. IPTC is looking for qualified developers to create the rules engine to accurately and efficiently categorize the documents using the rules.
Please consult this page for more information and to let us know if you’re interested in being considered.
Questions? Contact us.
Twitter: @IPTC
LinkedIn: IPTC