Categories
Archives
The IPTC NewsCodes Working Group is pleased to present the Q1 2025 release of IPTC NewsCodes.
As usual, most of the updates are in our flagship subject vocabulary, Media Topics.
Media Topic updates
This release adds 8 new concepts, retires 17 concepts, modifies 43 label names and 64 definitions, adds 10 notes (mostly to retired concepts), makes 28 hierarchy moves and modifies 7 wikidata mappings.
The new and modified terms have already been translated into Swedish (lang=se) and Norwegian (lang=no-NB and lang=no-NN)
New concepts (8 terms)
zoning policy, political party, political movement and association, communism, democratic socialism, theocracy, absolute monarchy, ski mountaineering
Note that ski mountaineering (medtop:20001390) has been added to the Media Topics vocabulary because it was added as a new sport for the 2026 Olympics.
Retired concepts (17 terms)
- civil and public service – use government employee (medtop:20000595) instead.
- military equipment – use military weaponry and equipment (medtop:20000602) instead.
- security measures (defence) – use national security (medtop:20000598) instead.
- national security (old) – Use national security (medtop:20000598) instead.
- public finance – Use government budget (medtop:20000607) or government debt (medtop:20000368) instead.
- government department – Use more specific terms or government (medtop:20000593) instead.
- safety of citizens – Use other terms such as public health (medtop:20001358) or emergency response (medtop:20000168) instead.
- interior policy – Use more specific terms instead.
- personal data collection policy – Use data protection policy (medtop:20000627) instead.
- planning inquiries – Use zoning policy (medtop:20001383), environmental policy (medtop:20000423) or other more specific terms instead.
- political crisis – Use more specific terms instead.
- political process – Use government (medtop:20000593) or other more specific terms instead.
- political parties and movements – Use political party (medtop:20001384) or political movement and association (medtop:20001385) instead.
- political development – Use politics (medtop:11000000) instead.
- civilian service – Use medtop:20001277 volunteering instead.
- integration policy – Use immigration policy (medtop:20000634) instead.
- regulatory authority – Use regulation of industry (medtop:20000636) instead.
Modified labels (43 terms)
politics and government, demonstration, government employee, public officials, constitution (law).
national security.military weaponry and equipment, head of state,local authority, minister or secretary (government), regional authority, taxation policy, data protection policy, immigration policy, summit meeting, treaty, foreign aid, international organisation, refugees and internally displaced people, non-governmental organisation (NGO), political prisoners and dissenters, cultural policy, sports policies, political party convention, political committee, head of government, border dispute, financial service, corporate bond, war victims, missing in action, breaking (breakdance), by-election, recall election, coalition building, zoning policy, political party, political movement and association, communism, democratic socialism, theocracy, absolute monarchy, ski mountaineering.
Modified definitions (64 terms)
politics and government, demonstration, computer networking, economic policy, environmental policy, healthcare policy, government, government employee, public officials, constitution (law), national security, armed forces, military weaponry and equipment, executive (government), government budget, head of state, local authority, minister or secretary (government), regional authority, taxation policy, government policy, nationalisation, privatisation, state-owned enterprise, data protection policy, policy towards indigenous people, pension and welfare policy, personal weapon control policy, immigration policy, nuclear policy, regulation of industry, food and drink regulations, international relations, diplomacy, summit meeting, treaty, economic sanction, foreign aid, international organisation, refugees and internally displaced people, non-governmental organisation (NGO), political prisoners and dissenters, lobbying, political system, democracy, dictatorship, cultural policy, sports policies, regional development policy, political party convention, head of government, infrastructure policy, economic development incentive, political leadership, border dispute, education policy, zoning policy, political party, political movement and association, communism, democratic socialism, theocracy, absolute monarchy, ski mountaineering.
Modified notes (10 terms)
safety of citizens, interior policy, personal data collection policy, planning inquiries, political crisis, political process, political parties and movements, political development, civilian service, integration policy.
Modified broader terms (hierarchy moves) (28 terms)
campaign finance, government employee, public officials, military weaponry and equipment, espionage and intelligence, data protection policy, housing and urban planning policy, policy towards indigenous people, pension and welfare policy, personal data collection policy, personal weapon control policy, planning inquiries, lobbying, political parties and movements, political development, political system, integration policy, regional development policy, infrastructure policy, political leadership, zoning policy, political party, political movement and association, communism, democratic socialism, theocracy, absolute monarchy, ski mountaineering.
Modified wikidata mappings: 7
political party, political movement and association, communism, democratic socialism, theocracy, absolute monarchy, ski mountaineering.
See the official Media Topic vocabulary on the IPTC Controlled Vocabulary server, and an easier-to-navigate tree view. An Excel version of IPTC Media Topics is also available.
Non-Media Topic changes
- New term: Software
- New terms: anonymised, recommended anonymisation
The IPTC Sports Content Working Group is proud to release version 1.1 of IPTC Sport Schema.
Documented at the dedicated site sportschema.org, Sport Schema is IPTC’s semantic web (RDF) based ontology for describing sports listings, results, statistics and even play-by-play actions during any kind of sports event.
Version 1.1 adds the following new features:
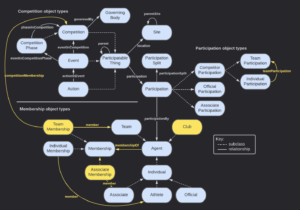
- We add a Club type, which can handle the organisation that hosts one or more teams of varying types, possibly across various sports. (Did you know that Bayern Munich has not just the famous men’s, women’s and junior football/soccer teams, but also basketball, handball, table tennis and even chess teams!)
- We also add a TeamMembership type, so a Team can be a member of a Club (and could theoretically move from one Club to another).
- We add support for the concept of “sports facets” that we originated in SportsML. (based on SportsML / NewsCodes facets) so we can now say that an event is “women’s 400 metres relay swimming”, not just “swimming”. The boxing example shows that the weight class of the event is “welterweight”.
- Added the ability to link from Athlete to Team via a new teamParticipation property.
- Add an AssociateMembership type so an Associate (such as a coach) can have a tenure relating to any Agent, including an Athlete or a Team. Previously Associates were linked to Teams via Participation objects which wasn’t satisfactory.
- Expanded and added to examples including a Boxing example showing how the new AssociateMembership type can be used to represent a coach or manager of an individual athlete (in this case a boxer)
- Added new golf ontology taking some properties from SportsML and some from the Golf vocabularies in IPTC NewsCodes. We have merged them together in Sport Schema for ease of use.
- Many cleanups to the SHACL Shapes used for validation of data.
Please take a look at Sport Schema and let us know what you think! We would love to hear about Sport Schema being implemented in real-world projects. Please contact IPTC using the Contact Us form or via the public discussion list at groups.io/g/iptc-sportsml/
At the IPTC Autumn Meeting, the IPTC Standards Committee voted on a change proposed by the Photo Metadata Working Group, which created version 2024.1 of the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard.
The change is minor but important to some: the definition of the Keywords property now includes the following text:
Keywords to express the subject and other aspects of the content of the image. Keywords may be free text and don’t have to be taken from a controlled vocabulary. Codes from the controlled vocabulary IPTC Subject NewsCodes must go to the “Subject Code” field.
This aligns the property definition with the way in which many photo agencies and photographers were already using the field: to convey aspects such as the lighting or lens effects used, “mood” of the image, dominant colour and more.
We give examples of how the Keywords property may be used in the IPTC Photo Metadata User Guide.
The relevant files have all been updated for the new version:
- The IPTC Photo Metadata Standard Specification
- The IPTC Photo Metadata User Guide
- The IPTC Photo Metadata TechReference, in both YAML and JSON formats
- The IPTC Photo Metadata Reference Image
We thank Agence France-Presse for their help in offering examples for how the Keywords property may be used.
The IPTC has worked together with the DPP and stakeholders from Reuters, Arqiva and Warner Brothers Discovery to develop a pioneering new initiative called DPP Live Production Exchange (LPX). The LPX protocol covers API and a data schema for information related to news coverage of live events, including the ability for B2B event subscribers to be informed about upcoming news events and their coverage.
IPTC’s contribution to the project was to enhance and evolve our ninjs (News in JSON) standard to support news coverage of events and live streamed content. The News in JSON Working Group dedicated a lot of its time to this work over the past two years, including participating in the DPP LPX Hackathon in Spring 2024.
The underlying data model for the events and planning work in ninjs comes from the IPTC News Architecture and is based on EventsML-G2, a part of the NewsML-G2 family of standards which was created over 10 years ago.
Ian Young of PA Media, Lead of the IPTC News in JSON Working Group, said “Basing the work of ninjs 3.0 on the stable foundation of the IPTC News Architecture made our work much simpler. IPTC members have been syndicating news events for years using this model so we know that it works. That meant that we could focus on making ninjs 3.0 handle live events and streaming video in a way that is practical and simple, both for developers and for users.”
IPTC Managing Director Brendan Quinn said “we owe our thanks to our teammates and partners on this project: David Thompson from IPTC liaison partners the DPP, JJ Eynon from CNN / Warner Brothers Discovery, Tania Vivero and Ian McLaren from Reuters (IPTC Voting Member), and Daniel Lynch from Arqiva (IPTC Associate Member). Through a very friendly and collegial but also productive and results-driven collaboration, we have arrived at a solution that should make syndicated news events much easier to handle in all newsroom workflows.”
ninjs 3.0 and the LPX API are or will soon be supported by tools from Arqiva, Reuters and Wolftech (who were recently acquired by Avid). We hope that many more implementations will be emerge in the coming months.
For more on ninjs 3.0, see the following resources:
- IPTC’s pages on ninjs (News in JSON)
- The ninjs generator tool, a simple form that generates sample ninjs documents in versions 1.5, 2.1 and 3.0
- The IPTC’s ninjs GitHub repository
- IPTC members regularly discuss ninjs at our News in JSON Working Group meetings and on the members-only News in JSON WG discussion group.
- Non-members are welcome to discuss ninjs at the public ninjs discussion group.

The IPTC NewsCodes Working Group is pleased to announce the latest release of the IPTC NewsCodes, our set of controlled vocabularies for the news industry.
Updates this time span many vocabularies, with the biggest updates to Media Topic and Digital Source Type.
Media Topic updates
Most of the recent work has been in the politics branch.
3 new concepts: by-election, recall election, coalition building
2 retired concepts: political campaigns, church elections
4 modified concept names (in English): voting system, referendum, fundamental rights, football (yes we finally refer to the sport as “football” in en-GB and “soccer” in en-US!)
Modified concept definitions: 22 civil rights, election, voting system, intergovernmental elections, local elections, primary elections, referendum, regional elections, voting, fundamental rights, censorship and freedom of speech, freedom of religion, freedom of the press, human rights, football, political debates, privacy, women’s rights, breaking (breakdance)
1 hierarchy move: fundamental rights has been moved from politics to society.
Also, the Wikidata mapping URIs have all been changed to point to the http:// version of the URI instead of the https:// version. This follows the official Wikidata guidance.
See the official Media Topic vocabulary on the IPTC Controlled Vocabulary server, and an easier-to-navigate tree view. An Excel version of IPTC Media Topics is also available.
Digital Source Type updates
5 new concepts have been added:
- Multi-frame computational capture sampled from real life, intended to cover media recorded by modern cameras and smartphones that may process several captured images together to create the saved media file, without any interaction with the photographer.
- Human-edited media, intended to replace the retired Original media with minor human edits, given that it is subjective to decide what is a “minor” edit.
- Digital creation, intended to replace the retired Digital art so that we can avoid the existential question of “what is art?”
- Screen capture, covering screenshots and screen recordings made on a device
- Composite of elements, as a generic form of the more specific “composite” terms.
2 concepts have been retired: Original media with minor human edits, and Digital art, as explained above.
8 concepts have had their names and definitions modified, while retaining the same machine-readable ID for backwards-compatibility purposes:
- Digital capture sampled from real life (ID: digitalCapture), replacing the previous name “Original digital capture sampled from real life”
- Digitised from a transparent negative (ID: negativeFilm), replacing the previous name “Digitised from a negative on film”
- Digitised from a transparent positive (ID: positiveFilm), replacing the previous name “Digitised from a positive on film”
- Digitised from a non-transparent medium (ID: print), replacing the previous name “Digitised from a print on non-transparent medium”
- Edited using Generative AI (ID: compositeWithTrainedAlgorithmicMedia), replacing the previous name “Composite with Trained algorithmic media”
- Algorithmically-altered media (ID: algorithmicallyEnhanced), replacing the previous name “Algorithmically Enhanced”
- Created using Generative AI (ID: trainedAlgorithmicMedia), replacing the previous name “Trained Algorithmic Media”
- Virtual event recording (ID: virtualRecording), replacing the previous name “Virtual recording”
Our thanks go to IPTC representatives and experts from Partnership on AI, Google, Adobe, C2PA, CIPA and many others on making these updates to our vocabulary, which is now widely used to identify Generative AI content.
Updates to other NewsCodes vocabularies
Alternative Identifier Role (altidrole)
- Vocabulary’s name changed to fix a spelling mistake.
- New concept: IPTC Video Metadata Hub ID (altidrole:vmhVideoId)
Event Occur Status (eocstat)
- Fix spelling mistake “occurence” -> “occurrence” throughout.
Golf Shot (spgolshot)
- New concept: Chip (spgolshot:chip)
Rights Property (rightsprop)
- New concept: Copyright Year (rightsprop:copyrightyear)
- 4 modified definitions: Minor Model Age Disclosure, Model Release Id, Model Release Status, Property Release Status.
Sports Concept (spct)
- New concept: Recurring Competition (spct:recurring-competition)
- New concept: Governing Body (spct:governing-body)
 The IPTC NewsCodes Working Group has released the latest update to IPTC NewsCodes vocabularies.
The IPTC NewsCodes Working Group has released the latest update to IPTC NewsCodes vocabularies.
The changes are quite minor this time, but we still recommend that users stay up to date with the latest version.
Changes to Media Topics vocabulary
Our main subject classification taxonomy, IPTC Media Topics, has seen the following updates:
1 new concept
- breaking (breakdance) (added earlier this year in time for the Paris 2024 Olympics)
1 retired concept
- missing in action (duplicate term added in error in the 2024 Q1 update. The existing term missing in action medtop:20000061 was moved to replace the newer term))
32 modified definitions
These changes mostly correct spelling errors in en-GB where US spellings had slipped in, such as changing “behavior” to “behaviour” for en-GB:
wireless technology, tobacco and nicotine, economic trends and indicators, international economic institution, stocks and securities, adult and continuing education, upper secondary education, social learning, medical condition, Confucianism, relations between religion and government, road cycling, competitive dancing, sexual misconduct, developmental disorder, fraternal and community group, cyber warfare, public transport, taxi and ride-hailing, shared transport, business reporting and performance, business restructuring, commercial real estate, residential real estate, podcast, financial service, business service, news industry, diversity, equity and inclusion, sustainability, profit sharing, breaking (breakdance).
As usual, the Media Topics vocabularies can be viewed in the following ways:
- In a collapsible tree view
- As a downloadable Excel spreadsheet
- On one page on the cv.iptc.org server
- In machine readable formats such as RDF/XML and Turtle using the SKOS vocabulary format: see the cv.iptc.org guidelines document for more detail.
Updates to other vocabularies
Horse Position (sphorposition)
New term “trainer” added to https://cv.iptc.org/newscodes/sphorposition. This term is needed by IPTC Sport Schema.
For more information on IPTC NewsCodes in general, please see the IPTC NewsCodes Guidelines.
The IPTC News Architecture Working Group is happy to announce the release of NewsML-G2 version 2.34.
This version, approved at the IPTC Standards Committee Meeting at the New York Times offices on Wednesday 17th April 2024, contains one small change and one additional feature:
Change Request 218, increase nesting of <related> tags: this allows for <related> items to contain child <related> items, up to three levels of nesting. This can be applied to many NewsML-G2 elements:
- pubHistory/published
- QualRelPropType (used in itemClass, action)
- schemeMeta
- ConceptRelationshipsGroup (used in concept, event, Flex1PropType, Flex1RolePropType, FlexPersonPropType, FlexOrganisationPropType, FlexGeoAreaPropType, FlexPOIPropType, FlexPartyPropType, FlexLocationPropType)
Note that we chose not to allow for recursive nesting because this caused problems with some XML code generators and XML editors.
Change Request 219, add dataMining element to rightsinfo: In accordance with other IPTC standards such as the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard and Video Metadata Hub, we have now added a new element to the <rightsInfo> block to convey a content owner’s wishes in terms of data mining of the content. We recommend the use of the PLUS Vocabulary that is also recommended for the other IPTC standards: https://ns.useplus.org/LDF/ldf-XMPSpecification#DataMining
Here are some examples of its use:
Denying all Generative AI / Machine Learning training using this content:
<rightsInfo> <dataMining uri="http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-AIMLTRAINING"/> </rightsInfo>
A simple text-based constraint:
<rightsInfo> <usageTerms> Data mining allowed for academic and research purposes only. </usageTerms> <dataMining uri="http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEECONSTRAINT" /> </rightsInfo>
A simple text based constraint, expressed using a QCode instead of a URI:
<rightsInfo> <usageTerms> Reprint rights excluded. </usageTerms> <dataMining qcode="plusvocab:DMI-PROHIBITED-SEECONSTRAINT" /> </rightsInfo>
A text-based constraint expressed in both English and French:
<rightsInfo> <usageTerms xml:lang="en"> Reprint rights excluded. </usageTerms> <usageTerms xml:lang="fr"> droits de réimpression exclus </usageTerms> <dataMining uri="http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEECONSTRAINT" /> </rightsInfo>
Using the “see embedded rights expression” constraint to express a complex machine-readable rights expression in RightsML:
<rightsInfo>
<rightsExpressionXML langid="http://www.w3.org/ns/odrl/2/">
<!-- RightsML goes here... -->
</rightsExpressionXML>
<dataMining uri="http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEEEMBEDDEDRIGHTSEXPR"/>>
</rightsInfo>
For more information, contact the IPTC News Architecture Working Group via the public NewsML-G2 mailing list.

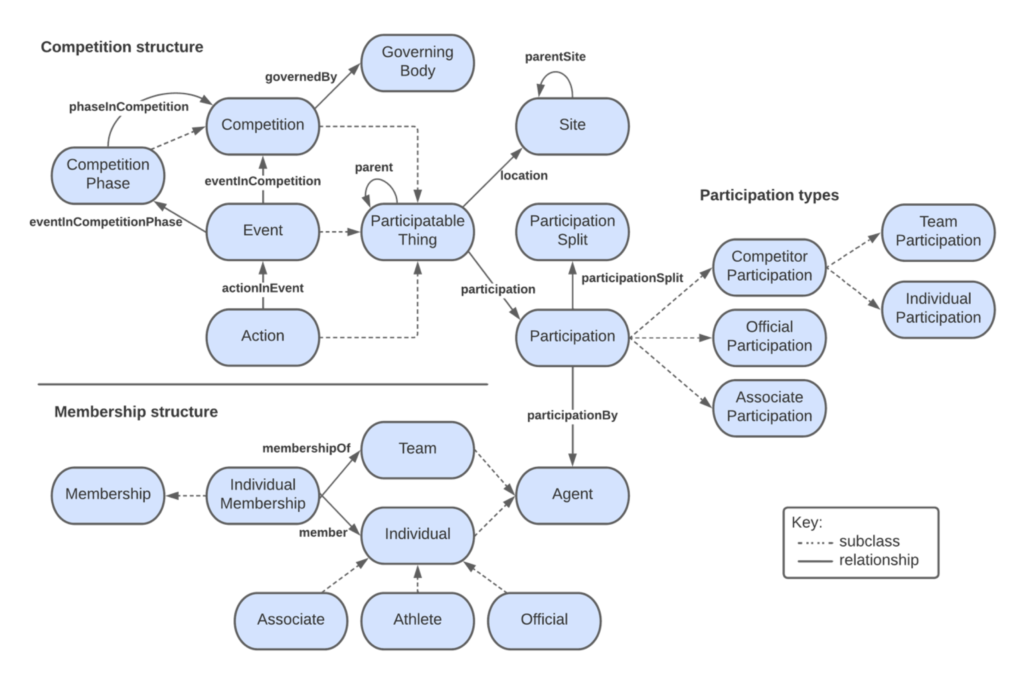
The IPTC Sports Content Working Group is happy to announce the release of IPTC Sport Schema version 1.0.
The first new IPTC standard to be released in more than 10 years, IPTC Sport Schema is a comprehensive model for the storage, transmission and querying of sports data. It has been tested on real-world use cases that are common in any newsroom or sports organisation.
IPTC Sport Schema has evolved from its predecessor SportsML. In contrast to the document-oriented nature of SportsML, IPTC Sport Schema takes a data-centric approach which is better suited to systems dealing with large volumes of data and also helps with integration across data sets.
“We reached out to many companies dealing with sports content and built up a clear picture of their needs,” says IPTC Sports Content Working Group lead Paul Kelly. “They wanted up-to-date formats, easy querying, the ability to handle e-sports and the ability to cross-reference between different media and data silos. IPTC Sport Schema addresses those requirements with a new basic model at the abstract end, and adhering to common use cases to keep things grounded.”
Content in Sports Schema is represented in the W3C’s universal Resource Description Framework (RDF), which renders any kind of data as a triple in the form of subject->predicate->object. Each component of a Sports Schema triple has a reference to an ontology, which defines the model at the heart of the standard. Querying is done using the W3C’s SPARQL standard, a kind of SQL for RDF.
“The IPTC has been working on RDF and semantic web standards for more than 10 years, going back to rNews and RightsML,” said IPTC Managing Director Brendan Quinn. “So we are very happy to release another semantic standard that can help organisations to publish and share sports data in a vendor-neutral, interoperable way.”
Being RDF-based, IPTC Sport Schema can be rendered in XML, JSON and the simple Turtle format, and can be converted easily between all three formats using free tools such as Apache Jena.
“Those familiar with SportsML or SportsJS should recognise the basic components of Sport Schema,” says Kelly, “both in the ontology and in the sports vocabularies introduced with SportsML 3.0, which were designed specifically with semantic technologies in mind.”
To support take-up and share information about the new standard, the IPTC has created a dedicated website, sportschema.org. The site contains:
- a list of use cases which were used to help design the schema and data structures
- example instance diagrams for various sports to help understand how the model can be applied to team, individual and other types of sports
- a data dictionary comparing IPTC Sport Schema to other prominent sport schemas (SportsML, ODF, BBC Ontology, etc.)
- A detailed and comprehensive IPTC Sport Schema ontology reference showing all classes, relationships and properties.
- A tool to validate Sport Schema data using the SHACL format to ensure RDF triples adhere to the specification (equivalent to XML Schema or JSON Schema)
- A tool to covert SportsML documents to IPTC Sport Schema data
- A set of unit tests and sample data files that were used to develop and maintain Sport Schema, including a bespoke unit test framework that ensures our example SPARQL queries continue to satisfy our use cases as the model evolves.
Those wishing to try out some SPARQL queries against some sports data should visit Sport Schema’s query endpoint. It includes example queries showing how to build a team roster, league standings and more from our sample data sets.
For more information on IPTC Sport Schema, see the IPTC’s landing pages on the IPTC Sport Schema standard, the standalone site sportschema.org, or the project’s GitHub repository.
If you are interested in joining those who are working on implementing IPTC Sport Schema in your project or your organisation, we would love to hear from you. Please contact us via IPTC’s contact form.

Made with Bing Image Creator. Powered by DALL-E.
Following the IPTC’s recent announcement that Rights holders can exclude images from generative AI with IPTC Photo Metadata Standard 2023.1 , the IPTC Video Metadata Working Group is very happy to announce that the same capability now exists for video, through IPTC Video Metadata Hub version 1.5.
The “Data Mining” property has been added to this new version of IPTC Video Metadata Hub, which was approved by the IPTC Standards Committee on October 4th, 2023. Because it uses the same XMP identifier as the Photo Metadata Standard property, the existing support in the latest versions of ExifTool will also work for video files.
Therefore, adding metadata to a video file that says it should be excluded from Generative AI indexing is as simple as running this command in a terminal window:
exiftool -XMP-plus:DataMining="Prohibited for Generative AI/ML training" example-video.mp4
(Please note that this will only work in ExifTool version 12.67 and above, i.e. any version of ExifTool released after September 19, 2023)
The possible values of the Data Mining property are listed below:
| PLUS URI | Description (use exactly this text with ExifTool) |
| Unspecified – no prohibition defined | |
| Allowed | |
| Prohibited for AI/ML training | |
|
http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-GENAIMLTRAINING |
Prohibited for Generative AI/ML training |
|
http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-EXCEPTSEARCHENGINEINDEXING |
Prohibited except for search engine indexing |
| Prohibited | |
|
http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEECONSTRAINT |
Prohibited, see plus:OtherConstraints |
|
http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEEEMBEDDEDRIGHTSEXPR |
Prohibited, see iptcExt:EmbdEncRightsExpr |
|
http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEELINKEDRIGHTSEXPR |
Prohibited, see iptcExt:LinkedEncRightsExpr |
A corresponding new property “Other Constraints” has also been added to Video Metadata Hub v1.5. This property allows plain-text human-readable constraints to be placed on the video when using the “Prohibited, see plus:OtherConstraints” value of the Data Mining property.
The Video Metadata Hub User Guide and Video Metadata Hub Generator have also been updated to include the new Data Mining property added in version 1.5.
We look forward to seeing video tools (and particularly crawling engines for generative AI training systems) implement the new properties.
Please feel free to discuss the new version of Video Metadata Hub on the public iptc-videometadata discussion group, or contact IPTC via the Contact us form.
The IPTC NewsML-G2 Working Group and the News Architecture Working Group are happy to announce the release of the latest version of our flagship XML-based news syndication standard: NewsML-G2 v2.33.
Changes in the latest version are small but significant. We have added support for the Digital Source Type property which is already being used in IPTC’s sister standards IPTC Photo Metadata Standard and IPTC Video Metadata Hub and ninjs. This property can be used to declare when content has been created or modified by software, including by Generative AI engines.
Examples of other possible values for the digital source type property using the recommended IPTC Digital Source Type NewsCodes vocabulary are:
| ID (in QCode format) | Name | Example |
| digsrctype:digitalCapture | Original digital capture sampled from real life:
The digital media is captured from a real-life source using a digital camera or digital recording device |
Digital video taken using a digital film, video or smartphone camera |
| digsrctype:negativeFilm | Digitised from a negative on film:
The digital image was digitised from a negative on film on any other transparent medium |
Digital photo scanned from a photographic negative |
| digsrctype:minorHumanEdits | Original media with minor human edits:
Minor augmentation or correction by a human, such as a digitally-retouched photo used in a magazine |
Original audio with minor edits (e.g. to eliminate breaks) |
| digsrctype:algorithmicallyEnhanced | Algorithmic enhancement: Minor augmentation or correction by algorithm |
A photo that has been digitally enhanced using a mechanism such as Google Photos’ “denoise” feature |
| digsrctype:dataDrivenMedia | Data-driven media: Digital media representation of data via human programming or creativity |
Textual weather report generated by code using readings from weather detection instruments |
| digsrctype:trainedAlgorithmicMedia | Trained algorithmic media: Digital media created algorithmically using a model derived from sampled content |
A “deepfake” video using a combination of a real actor and a trained model
|
The above list is a subset of the full list of recommended values. See the full IPTC Digital Source Type NewsCodes vocabulary for the complete list.
Guidance on using Digital Source Type
The IPTC Photo Metadata User Guide contains a section on Guidance for using Digital Source Type including examples for various types of media, including images, video, audio and text. The examples referenced in this guide can also apply to NewsML-G2 content.
Where Digital Source Type can be used in NewsML-G2 documents
The new <digitalSourceType> property can be added to the contentMeta section of any G2 NewsItem, PackageItem, KnowledgeItem, ConceptItem or PlanningItem to describe the digital source type of an item in its entirety.
It can also be used in the partMeta section of any G2 NewsItem, PackageItem or KnowledgeItem to describe the digital source type of a part of the item. In this way, content such as a video that includes some captured shots and AI-generated shots can be fully described using NewsML-G2.
Find out more about NewsML-G2 v2.33
All information related to NewsML-G2 2.33 is at https://iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/2.33/.
The NewsML-G2 Specification document has been updated to cover the new version 2.33.
Example instance documents are at https://iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/2.33/examples/.
Full XML Schema documentation is located at https://iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/2.33/specification/XML-Schema-Doc-Power/
XML source documents and unit tests are hosted in the public NewsML-G2 GitHub repository.
The NewsML-G2 Generator tool has also been updated to produce NewsML-G2 2.33 files using the version 38 catalog.
For any questions or comments, please contact us via the IPTC Contact Us form or post to the iptc-newsml-g2@groups.io mailing list. IPTC members can ask questions at the weekly IPTC News Architecture Working Group meetings.