Categories
Archives
The comprehensive NewsML-G2 Guidelines are available now in an updated version and anybody can read them on the web: https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/
What has been modified:
- The changes of the NewsML-G2 version 2.24 and 2.25 are covered, see https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/#whats-new-in-newsml-g2-2.5-including-version-2.24
- Some details have been improved, we try to make the guidelines as unambiguous as possible.
- The Quick Start Guides for text, photo/graphics, video and packages have been merged into the web document.
How to use the new Guidelines:
- Quick Start with NewsML-G2 Basics: https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/#quick-start-guide-to-newsml-g2-basics
- Quick Start with text news: https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/#quick-start-text
- Quick Start with photo/graphics: https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/#quick-start-pictures-and-graphics
- Quick Start with video: https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/#quick-start-video
- Quick Start with packages: https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines/#quick-start-packages
- The Guidelines start at https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/guidelines – a full table of content is made available in a sidebar or in the top region.
- Printing the Guidelines is supported: use the Print function of your browser and you should get a very print-friendly rendition of the document. Be aware: about 300 pages.
We welcome feedback on the format and the content of the Guidelines. Use the Contact Us form.

Photo credit: Jill Laurinaitis
By Stuart Myles
Chairman of the Board of Directors, IPTC
IPTC holds face-to-face meetings in several locations throughout the year, although, most of the detailed work of the IPTC is now conducted via teleconferences and email discussions. Our Annual General Meeting for 2017 was held in Barcelona in November. As well as being the time for formal votes and elections, the AGM is a chance for the IPTC to look back over the last year and to look ahead about what is in store. What follows are a slightly edited version of my remarks at IPTC’s AGM 2017 in Barcelona.
IPTC has had a good year – the 52nd year for the organization!
We’ve updated our veteran standards, Photo Metadata – our most widely-used standard – and NewsML-G2 – our most comprehensive XML standard, marking its 10th year of development.
We’re continuing to work in partnership with other organizations, to maximize the reach and benefits of our work for the news and media industry. In coordination with CEPIC we organized the 10th annual Photo Metadata Conference, looking to the future of auto tagging and search, examining advanced AI techniques – and considering both their benefits and their drawbacks for publishers. With the W3C we have crafted the ODRL rights standard and are launching plans to create RightsML as the official profile of the ODRL standard, endorsed by both the IPTC and W3C.
We’ve also tackled problems that matter to the media industry with technology solutions which are founded on standards, but go beyond them. The Video Metadata Hub is a comprehensive solution for video metadata management that allows exchange of metadata over multiple existing standards. The EXTRA engine is a Google DNI sponsored project to create an open source rules based classification engine for news.
We’ve had some changes in the make-up of IPTC. Johan Lindgren of TT joined the Board. Bill Kasdorf has taken over as the PR Chair. And we were thrilled to add Adobe as a voting member of IPTC, after many years of working together on photo metadata standards. Of course, with more mixed emotions, we have also learnt that Michael Steidl, the IPTC Managing Director, for 15 years will retire next Summer. As has been clear throughout this meeting and, indeed, every day between the meetings on numerous emails and phone calls, Michael is the backbone of the work of the IPTC. Once again, I ask you to join me in acknowledging the amazing contributions and dedications that Michael displays towards the IPTC.
Later today, we will discuss in detail our plans to recruit a successor for the crucial role of the Managing Director. And this is not the only challenge that the IPTC faces. We describe ourselves as “the global standards body of the news media” and that “we provide the technical foundation for the news ecosystem”. As such, just as the wider news industry is facing a challenging business and technical environment, so is the IPTC.
During this meeting, we’ve talked about some of the technical challenges – including the continuing evolution of file formats and supporting technologies, whilst many of us are still working to adopt the technologies from 5 or 10 year ago. We’ve also talked about the erosion of trust in media organizations and whether a combination of editorial and technical solutions can help.
But I thought I would focus on a particular shift in the business and technical environment for news that may well have a bigger impact than all of those. That shift can be traced back to 2014 which, by coincidence, is when I became Chairman of the IPTC. Last week, Andre Staltz published an interesting and detailed article called “The Web Began Dying in 2014, Here’s How“. If you haven’t read it, I recommend it. The article makes a number of interesting points and backs them up with numerous charts and statistics. I will not attempt to summarize the whole thing, but a few key points are worth highlighting.
Staltz points out that, prior to 2014, Google and Facebook accounted for less than 50% of all of the traffic to news publisher websites. Now those two companies alone account for over 75% of referral traffic. Also, through various acquisitions, Google and Facebook properties now share the top ten websites with news publishers – in the USA 6 of the 10 most popular websites are media properties. In Brazil it is also 6 out of 10. In the UK it is 5 out of 10. The rest all belong to Facebook and Google.
Both Facebook and Google reorganized themselves in 2014, to better focus on their core strengths. In 2014, Facebook bought Whastapp and terminated its search relationship with Bing, effectively relinquishing search to Google and doubling down on social. Also in 2014, Google bought DeepMind and shutdown Orkut, its most successful social product. This, along with the reorganization into Alphabet, meant that Google relinquished social to Facebook and allowing it to focus on search and – even more – artificial intelligence. Thus, each company seems happy to dominate their own massive parts of the web.
But … does that matter to media companies? Well, Facebook said if you want optimal performance on our website, you must adopt Instant Articles. Meanwhile, Google requires publishers to use its Accelerated Mobile Pages or “AMP” format for better performance on mobile devices. And, worldwide, Internet traffic is shifting from the desktop to mobile devices.
Then, if you add in Amazon, Apple and Microsoft, it is clear that another huge shift is going on. All of the Frightful Five are turning away from the Web as a source of growth and instead turning to building brand loyalty via high end devices. Following the successful strategy of Apple, they are all becoming hardware manufacturers with walled gardens. Already we have Siri, Cortana, Alexa and Google Home. But also think about the investments going on by these companies in AR and VR as ways to dominate social interactions, e-commerce and machine learning over the Internet.
So, just as news companies must confront these shifts in the global business and technology environment, so must the IPTC. During this meeting, we’ve talked about our initial efforts to grapple with metadata for AR, VR and 360 degree imagery. We’ve also discussed techniques which are relevant to news taxonomy and classification, including machine learning and artificial intelligence. At the same time, Facebook, Google and others are not totally in control, as they – along with Twitter – found themselves having to explain the spread of disinformation on their platforms and under increased government scrutiny, particular in the EU. So, all of us, whether we describe ourselves as news publishers or not, are dealing with a rapidly changing and turbulent information, technical and business environment.
What does this mean for IPTC? IPTC is a news technology standards organization. But it is also unique in that we are composed of news companies from around the world. We know from the membership survey that both of these factors – influence over technical solutions and access to technology peers from competitors, partners, diverse organizations large and small – are very important to current members. In order to prosper as an organization, IPTC needs to preserve these unique benefits to members, but also scale them up. This means that we need to find ways to open up the organization in ways that preserve the value of the IPTC and fit with the mission, but also in ways that are more flexible. We need to continue to move beyond saying that the only thing we work on is standards and instead use standards as a component of the technical solutions we develop, as we are doing with EXTRA and the Video Metadata Hub. We need to work with diverse groups focused on solving specific business and journalistic problems – such as trust in the media – and in helping news companies learn the best ways to work with emerging technologies, whether it is voice assistants, artificial intelligence or virtual reality.
I’m confident that – working together – we can continue to reshape the IPTC to better meet the needs of the membership and to move us further forward in support of solving the business and editorial needs of the news and media industry. I look forward to working with all of you on addressing the challenges in 2018 and beyond.
Stuart Myles is the Director of Information Management at Associated Press.
An updated version 2.26 of NewsML-G2 is available as Developer Release
- XML Schemas and the corresponding documentation are updated
- the Structure Matrix Excel sheet is updated
Packages of version 2.26 files can be downloaded:
- All XML Schemas plus Structure Matrix (about 60MB) from https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/NewsML-G2_2.26.zip
- The same without XML Schema documentation in HTML (about 1MB) from https://www.iptc.org/std/NewsML-G2/NewsML-G2_2.26-noXMLdocu.zip
- New: in the newsml-g2 repository on GitHub: https://github.com/iptc/newsml-g2
All changes of version 2.26 can be found on that page: http://dev.iptc.org/G2-Approved-Changes
Reminder of an important decision taken for version 2.25 and applying to version 2.26 too: the Core Conformance Level will not be developed any further as all recent Change Requests were in fact aiming at features of the Power Conformance Level, changes of the Core Level were only a side effect.
The Core Conformance Level specifications of version 2.24 will stay available and valid, find them at http://dev.iptc.org/G2-Standards#CCLspecs

By Johan Lindgren
The Sports Content Working Group of IPTC started in the early 2000’s, initially to develop the XML standard SportsML. But the group has evolved to handle many aspects of reporting sports in the news.
The initial big question for news organisations handling sports is to decide if it should be handled as text or as data. The sports articles have, obviously, more in common with articles about other subjects. It is the results, schedules, statistics and standings that provide the dilemma. You can choose to provide the results ready for display on screen or on paper. Or you can provide the results as detailed marked up data and let the receiver handle the formatting, depending on purpose.
In fact, with using both NewsML-G2 and SportsML from IPTC you can provide both variants in parallel, if you wish so. In a NewsML-G2 news item as wrapper you provide one rendition of the content with the results as data in SportsML markup, and in another rendition you provide the same results, but in a displayable format like HTML5.
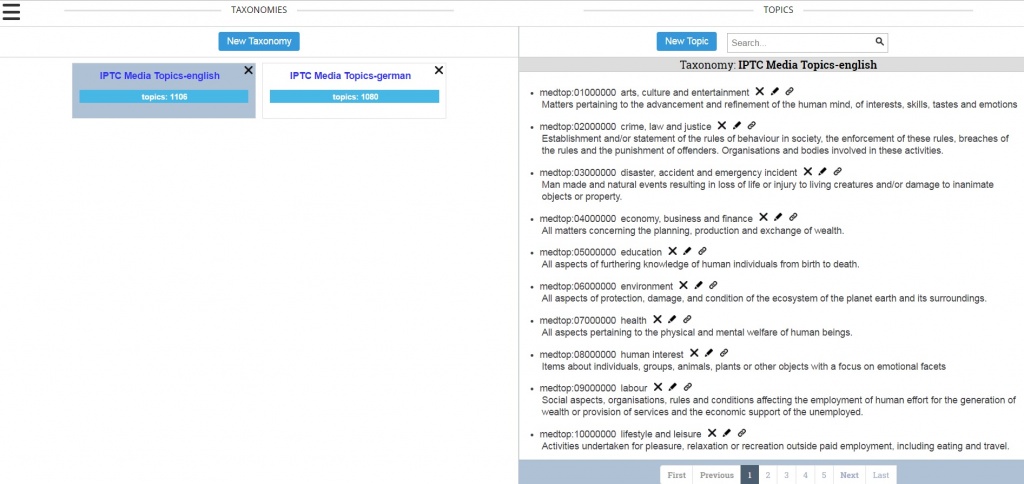
Vocabularies and Media Topics
Another big issue in handling sports data is knowing all the terms, what they mean and how they are used. The people in the sports group have spent a lot of time on this and provide very extensive vocabularies. Some are found in the Media Topics, maintained by the NewsCodes Working Group of IPTC. The same is true for the new addition to this, called facets. Facets refine the semantics of a Media Topic.
Example: If you try to combine Nordic skiing, female, relay, freestyle, 4×5 km as constituting one combined Media Topic and think of all the variations resulting from alternates to those terms, and then expand that thought to all sports events, the number of Media Topics will be overwhelming. Instead, IPTC chose to minimize the number of Media Topics and instead create a system of facets that qualify these broader topics. So, for example, “male” and “female” can apply to many, many sport competition topics, eliminating the need to create separate Media Topic terms for all of them.
About SportsML
Apart from the topics and their facets there is a huge number of metadata property values maintained by the sports group. These values are listed in 113 vocabularies (they can be downloaded), 37 of them are used for the core of SportsML and the other 76 are used for sport-specific additions. In total there are 1,850 values defined and listed as concepts in 113 knowledge items. The list of metadata values and their explanations is fundamental know-how in the sports reporting. You can have names and definitions in several languages.
Example of a code saying the player started the game on the field:
<concept id=”spplayerstatusstarter”>
<conceptId qcode=”spplayerstatus:starter” />
<name xml:lang=”en-US”>starter</name><name xml:lang=”en-GB”>starter</name>
<definition xml:lang=”en-GB”>A member of the lineup that enters the field at the commencement of play.</definition></concept>
SportsML is used by news organisations around the world both for everyday sport reporting and big events. BBC, for example, built their handling of the Olympic results in London around SportsML. It is also used by organisers of so-called fantasy sports leagues. Even by just using the core you can handle most normal news reporting of all sports events and competitions. There are also plugins for eleven sports, when you want to handle very in-depth data of these sports. And more plugins can be added. There are also ways to extend the standard with your own values or constructs. When developing SportsML the aim has always been to handle things in the core if the things are applicable to more than one sport. But some things are very specific to one sport and will instead be placed in its own schema which is imported and linked in proper places.
To illustrate this we can use this snippet from a soccer game:
<team-stats score=”0″ score-opposing=”2″ event-outcome=”speventoutcome:loss”>
<team-stats-soccer line-formation=”433″>
<stats-soccer-offensive corner-kicks=”2″/>
The first line is general with the score and outcome. But the two other lines are soccer-specific with a line-formation and the number of corner-kicks this team shot in this game.
SportsML for JSON
Up until now SportsML has mainly been serialized using XML. But with increasing interest in JSON the sports group is working on also providing a schema of SportsML for JSON usage. The work is close to being ready for the first public release. Some details of the schema need to be finalized and then the Working Group provide samples and some tools. We’re hoping to have this ready to release by early 2018.
The release of 3.0 of SportsML in XML also provided some tools (see our Github repository), mainly to transform between the earlier version, 2.2, and 3.0. One of the big developments in 3.0 was the possibility to handle statistics either in generic structures or in specific structures. So there are tools to transform between the two variants. To show this we can compare the above soccer example with the similar generic sample:
<stat stat-type=”spsocstat:line-formation” value=”433″/>
<stat class=”spct:offense” stat-type=”spsocstat:corner-kicks” value=”2″/>
As you see the attribute names become type-values in the generic stat-construction.
The work in the Sports Content Group is completely done by volunteers. The members of the group work in the news business and contribute to the group as much as their work allows. We welcome all interested persons, e.g. by joining our public discussion forum. The more people who can contribute the better, and there seem to be a never-ending flow of interesting topics when you start talking about sports data.
Johan Lindgren is the Chair of the Sports Content Working Group and a developer at TT Nyhetsbyrån, Sweden.
Our current Managing Director Michael Steidl is retiring in the summer of 2018 after 15 years of dedicated service to the IPTC. The IPTC is now seeking applicants to be the next Managing Director of our organization. Feel free to contact Michael (office@iptc.org) or our Chair, Stuart Myles, (chair@iptc.org) if you have any questions.
Job Opportunity: Managing Director of IPTC
For more information about the position, read the full Managing Director profile.
The IPTC is seeking applications for the next Managing Director of our organization. We are the global standards body of the news media and provide the technical foundation for the news ecosystem. Our mission is to simplify the distribution of information. We develop and promote efficient technical standards to improve the management and exchange of information between content providers, intermediaries and consumers.
The Managing Director, working with the Board and Membership, seeks to broaden adoption of IPTC standards, to maximize information sharing between members and to collaborate with partners across the news and media industry. The ideal applicant will have a strong record of working with news technology, presenting a positive image of an organization and administering a membership or non profit organization.
Learn more about IPTC and read the full Managing Director profile.
Applicants should email a letter of interest, curriculum vitae and contact information for three references to office@iptc.org. We will start considering applications on 1 December 2017.
By Jennifer Parrucci
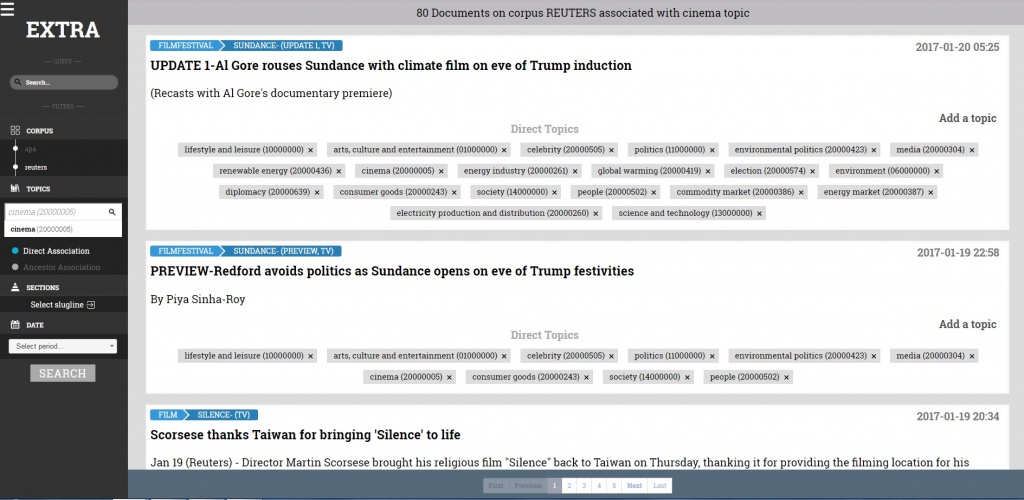
In leading the way for the creation of a rule-based, multilingual classification system, the IPTC’s EXTRA (EXTraction Rules Apparatus) project is providing a powerful and innovative way for publishers to classify documents using the industry standard IPTC Media Topics taxonomy, as well as tailor rules to their own existing taxonomies. By making these powerful capabilities freely available to the global news publishing community, the EXTRA project catalyzes a variety of innovative outcomes including intelligent aggregation, search and analytics.
In 2016, the IPTC received a €50,000 grant from Google’s Digital News Initiative to create EXTRA , an open source, rules-based, classification system for the annotation of news documents with high-quality subject tags that can be used by publishers to deliver valuable services including, but not limited to, subject related content streams and collections, advertising targeting and content recommendations.
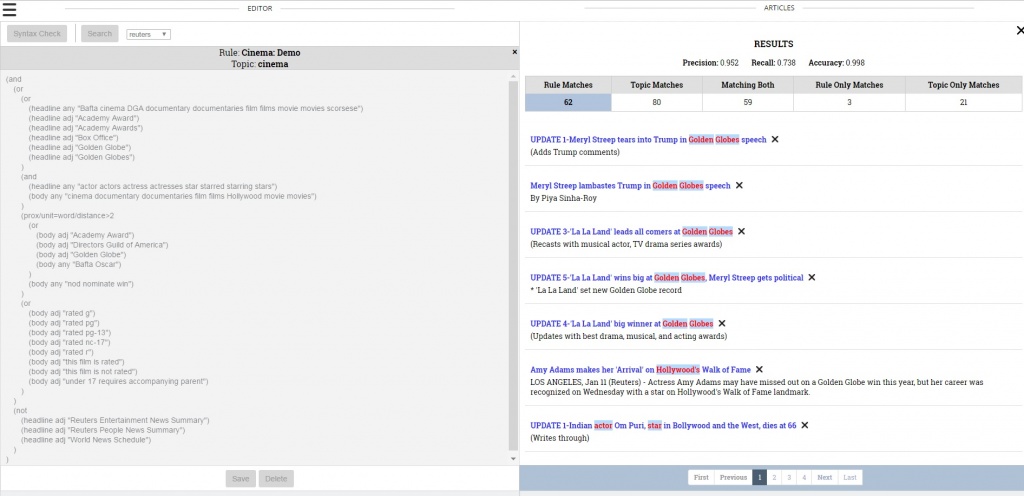
While EXTRA is still in development, attendees of the IPTC Spring Meeting in London were treated to an update and EXTRA demo. The group was shown the rule writer tools and interface and given an example of how to write and test rules. Feedback on these tools is welcomed – the EXTRA project is available via github, including the Extra User Manual, the Extra core code and the Extra API and UI.
A Rules-Based System Improves Tag Consistency Over Other Methods
The fact that EXTRA is rules-based, rather than relying on hand-tagging or statistics-based machine learning systems on the other, is key. EXTRA’s rules-based system allows publishers to improve tag consistency over hand-tagging methods, and provides much more rapid and scalable functionality. EXTRA also allows publishers to adapt their tagging for breaking new and low-frequency topics that cannot be captured by statistical approaches that require numerous annotated results. Users of EXTRA can tweak and customize the extraction rules to suit the needs and patterns of their publication and will be able to either use the IPTC Media Topics as the basic vocabulary or load their own taxonomies into the software. And unlike machine learning, which is a “black box,” EXTRA makes it easier to explain why a given classification was used, and to precisely explain–and correct–mistakes.
A team of IPTC members began by creating a technical requirements document for the project. System requirements included that the tool could be easily configured by given taxonomy, corpora and rules schema, that a comprehensive query language for rules creation was decided upon, that document classification resulted in high precision and recall scores, that the classification could be done in multiple languages, that the system and UI were intuitive and transparent and that everything be available through an open MIT license.
After an extensive search, IPTC hired Infalia in January 2017 to develop the software for EXTRA. Two linguists, one for German and one for English, were hired to create sample rules based on the IPTC Media Topics. The Austrian Press Agency (APA) and Reuters licensed corpora to be used for the EXTRA development process and as examples for users. The working version of EXTRA was completed at the end of June 2017.
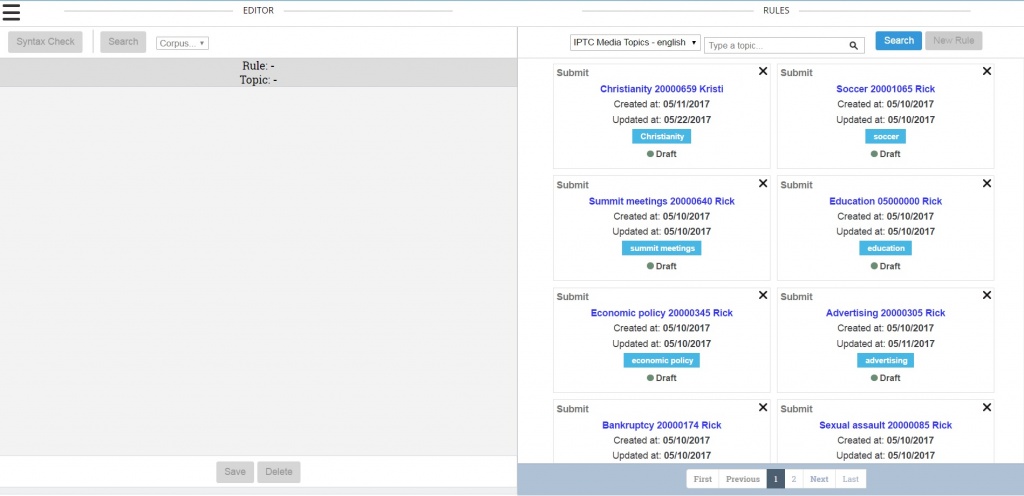
Demo of EXTRA: Taxonomy Management Feature
On May 16, 2017 attendees of the IPTC Spring Meeting in London were treated to an EXTRA demo and update about the project. During the demo, the group was shown the rule writer tools and interface and given an example of how to write and test rules.
The group was first shown the taxonomy management feature. For the demo, we pre-loaded the taxonomy management module with the IPTC Media Topics in both English and German. Users are free to use whatever taxonomies they would like. If a taxonomy is selected, one will be able to see the terms in that taxonomy along with their term definitions. The user will also be able to edit and delete terms from that taxonomy.
To assist the linguists in writing rules, they used the document search to see what articles within the corpora returned for each Media Topic. This process provided insights into keywords, phrases and article structures that could alert the engine that an article was about a particular topic, and enabled refinement of the rules or the vocabularies. Users can see the IPTC NewsML-G2 XML of a selected document to see what fields they might want to leverage in the rule.
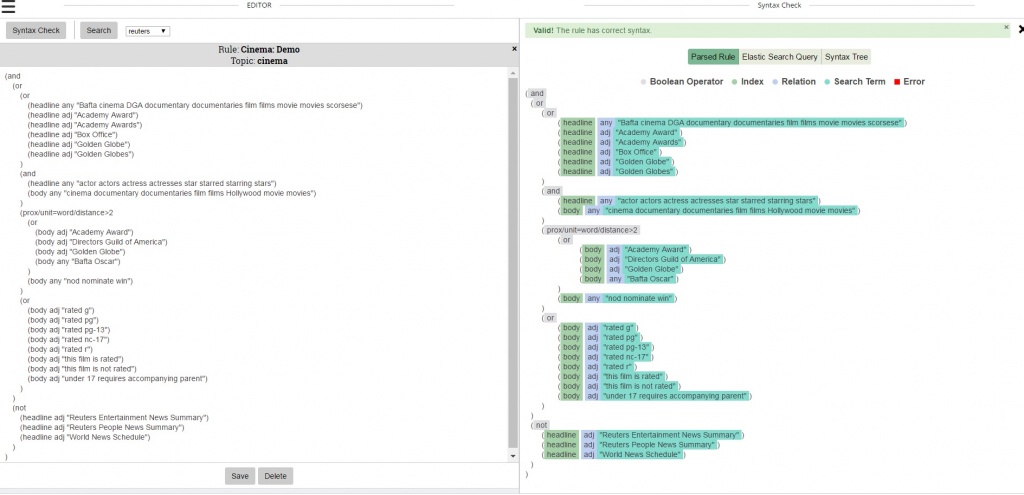
Sample rules
It was then time to show some sample rules. The EXTRA Query Language enables rule writers to create rules that analyze the text of the documents using ElasticSearch operators plus some custom ones. It allows for stemming by language, querying by a whole document or tokenized by a sentence, paragraph or headline. Rules can be written to target the proximity of words or phrases from each other, whether in the document as a whole or a specific field, the frequency of words or phrases individually or how many words from a list appear.
Examples of simple rules:
A rule that requires that “play” and “bass drum guitar piano” appear in proximity of 3 words
(prox/unit=word/distance<=3
(text_content any/stemming “play”)
(text_content any/stemming “bass drum guitar piano”)
)
A rule that requires that “Merkel” and “Obama” appear in the same paragraph
(prox/unit=paragraph/distance=1
(body = “Merkel”)
(body = “Obama”)
After writing a rule, the user has the ability to syntax check their work.
Then, one can run the rule against a corpus to see how many articles match the rule and were tagged with that term (if it is a pre-existing tag), how many many articles only matched the rule and how many articles matched the rule and not the tag. The user is also shown precision and recall scores. All of this data allows the user to tweak their rule until they are happy with the result.
While EXTRA was still in development at the time of the EXTRA demo, the response from the room was positive and members were eager for the finished product.
Feedback on EXTRA:
The EXTRA project is available via github, including the Extra User Manual, the Extra core code and the Extra API and UI.
Please send your feedback about EXTRA to office@iptc.org.
Jennifer Parrucci is a the group lead for IPTC’s News Codes Working Group and a Senior Taxonomist for NYTimes.com.
A ODRL (Open Rights Digital Language) Candidate Recommendation was released by W3C’s Permissions & Obligations Expressions (POE) Working Group on 26 September: ODRL has been updated to a generic information model that can be customized by any industry or business sector. IPTC is looking for members and experts with experience in defining licensing information in a machine-readable way to help adapt IPTC’s RightsML standard according to the new ODRL Recommendation, which will specifically address the needs of the news industry.
IPTC’s RightsML – https://iptc.org/standards/rightsml/ – is a standard providing a data model for marking up rights expressions about content of all relevant media types in a machine-readable way. The standard was introduced in 2012 and from the start it was built on ODRL – Open Digital Rights Language – a rights expression framework defined outside IPTC. At that time, a W3C Community Group was backing ODRL.
In early 2016 W3C established a formal Permissions & Obligations Expressions (POE) Working Group – https://www.w3.org/2016/poe/charter – to make a W3C Recommendation from the Community Group specifications, and on 26 September a Candidate Recommendation was released. The work on that W3C Recommendation will be closed by the end of 2017, and IPTC will take action to align a next RightsML version with the Recommendation.
IPTC Action: Update RightsML by Synchronising It With the New W3C Recommendation as ODRL RightsML Profile
The transfer of ODRL from a Community Group to a Recommendation approved by the W3C Consortium was not only a copy and paste action. The basic design has not been changed but the status of many actions, constraints or party functions has been changed from “normative” to “non-normative.” The reason was to make the ODRL Recommendation a generic information model which can be easily adapted to the different needs of various business sectors. This has been demonstrated by the range of participants of the W3C Working Group covering needs and interests from media companies and their trade associations, financial data providers, and universities.
The solution for that is called ODRL Profile: it defines all the actions, kinds of constraints, types of involved parties and more which are typical to a business sector and these definitions are add-ons to the basic Information Model of the Recommendation. This also slims down the specifications: businesses behind media assets don’t have to take care of the requirements regarding e.g. scientific papers.
IPTC has taken the role of defining the RightsML Profile of ODRL covering the needs of the news industry. Writing down the definitions fitting into the context of ODRL will not be that hard. Michael Steidl and Stuart Myles of the IPTC are invited experts of the ODRL/POE Working Group and have been active in its development from the start.
The big challenge is to determine which business needs of the news industry should be covered by the actions, constraints or parties defined by the RightsML Profile. To achieve that we need people from IPTC members and experts from other companies who have any experience in defining licensing information in a machine-readable way. Regular conference calls will take place from October 2017 to early 2018 to select and define what should be included to update RightsML Profile.
ODRL: From Candidate Recommendation to the Final Recommendation
On 26 September 2017, W3C published the Candidate Recommendation of ODRL. Links to the relevant W3C documents and other relevant resources are provided in the Details section below.
This opens a test phase until mid-November; in this period the Information Model and Vocabulary documents should be reviewed and comments may be posted. Further, W3C procedures specify that the Information Model and Vocabulary should be implemented into software at least by two parties and be tested against a list of criteria. Any party interested in ODRL and all IPTC members are invited to take this action. For more information contact Michael Steidl (mdirector@iptc.org).
Details for Creating the RightsML ODRL Profile:
- POE Working Group Charter: https://www.w3.org/2016/poe/charter
- POE Working Group home page: https://www.w3.org/2016/poe/wiki/Main_Page
- ODRL Information Model – Candidate Recommendation: https://www.w3.org/TR/2017/CR-odrl-model-20170926/
- ODRL Vocabulary – Candidate Recommendation: https://www.w3.org/TR/2017/CR-odrl-vocab-20170926/
- RightsML Profile outline: http://w3c.github.io/poe/rightsml/ (currently only the section heads are shown)
- The RightsML landing page of the IPTC website: https://iptc.org/standards/rightsml/
- The current RightsML on the IPTC Developer Site: http://dev.iptc.org/RightsML
- The current and small RightsML specification document: http://www.iptc.org/std/RightsML/1.1/RightsML_1.1EP2-spec_1.pdf
- IPTC contact: Michael Steidl – mdirector@iptc.org
IPTC’s Board of directors and Michael Steidl jointly announce that Michael will retire from employed work in mid-2018 and he will step down as IPTC’s Managing Director by then.
The Board has already started to make plans for selecting a new IPTC Managing Director and will provide more details in a separate communication.
Stuart Myles
Chairman of the IPTC Board
Being IPTC’s Managing Director for 15 years is a great experience and I’m happy about having been involved in the development and roll-out of 9 new standards, the new Media Topic taxonomy and other vocabularies; further in setting up new formats of the face -to-face meetings and in the creation of new types of meetings. Being in contact with our membership is also part of the bright side of my IPTC life and I enjoyed spreading the word about IPTC and its work among people knowing only little or nothing about our organisation. It was great to welcome 74 new members in this period.
Unfortunately, even such a great period of life started to apply burden on me, so I’ve decided to retire from employed work next summer. Please look forward to what the future will bring.
Michael Steidl
Managing Director of IPTC
IPTC holds its Autumn Meeting this year in Barcelona, Spain, from Monday, 6 November, through Wednesday, 8 November.
A team of IPTC Leads is working on the topics of the Autumn Meeting and we have already a very exciting list:
- Discussion topic: The Art and Science of Practical Metadata
- Discussion topic: System Vendors and News Exchange
- Discussion topic: Automating News – Speed is nothing without Accuracy
- Discussion topic: Trust in the Media
- Discussion topic: JSON – Man for all Seasons?
- Sessions of the NewsML-G2, ninjs, NewsCodes, Video/Photo Metadata and Rights Expression Working Groups; and of the Public Relations and the Standards Committee
- Annual General Meeting
By Sarah Saunders
Ten years ago, the very first IPTC Photo Metadata Conference in Florence was packed with photographers and picture libraries eager to discuss ways of protecting their work in the digital environment. The image industry has expanded enormously since. The image industry has the additional challenge of vast numbers of images crowding the web, and the difficulty of finding the relevant picture, as well as the metadata relating to it.
IPTC Photo Metadata Conference 2017 was designed to look into the future, with a focus on image search using AI or Artificial Intelligence. The ability of computer systems to learn from humans has increased enormously in recent years, and the necessary computer power has now become available. The question for the conference was – how far can these systems help the professional image industry sharpen up its search capability and make gains in productivity?
Solution for Auto Tagging in the Image Industry
Kai-Uwe Barthel, professor of visual computing at HTW Berlin University gave a clear exposition on the history of the field and of the pressing need to create solutions for the picture industry. There are now too many images for classical search systems to handle, but using Neural Network Analysis – a variant of AI – computer systems can be taught to tag and recognise images in a fraction of the time it takes to manually tag. As most online images are untagged, a combination of human tagging and visual similarity search presents a viable way forward. But Barthel and his team have also researched new methods of presenting images, using three dimensional structures to dig into results with large numbers of images visible at one time.
Speakers on the use of AI came from across the industry, presenting solutions which can be put into practice now. The key to success in this area is to have enough content for the computers to learn from, and this can be achieved in a number of different ways. General AI systems produce good results for skies and beaches and general themes because they’ve had the data to learn from. But users can set a system to learn from their own content so that more specialist content can be tagged if the conditions are right. Computers are learning faster, and need fewer images to learn from than before.
AI systems can be trained to recognise faces, text, colours, composition, scenes, and objects, but can also be trained in the aesthetics of image selection, with one speaker maintaining that twenty images are enough to train a system in a particular brand aesthetic. But speakers admitted also that defining the precise location of what is shown in an image by its content was tested but it did not work in a reliable way.
Speakers stressed that the important element in computer learning is the understanding of the nature of the material to be tagged, an attribute which is currently not about to be taken over by artificial intelligence. The benefits in speed and productivity will be enormous but we’re not yet talking about doing away with human skills altogether!
IPTC Video Metadata and Easier Cross Media Distribution
The first afternoon session by IPTC Managing Director Michael Steidl was about the IPTC Video Metadata Hub (VMH), published in 2016 to provide a standard set of fields for use across the varied technologies used in video. Many of the Video Hub fields are equivalent to those in IPTC Photo Metadata Standard, which helps streamline cross media distribution. The VMH can be applied down to the level of video clips, which makes it a useful metadata tool for production, archive and distribution.
Technology That Protects Rights Information in Google Image Search
The IPTC conference was held a day after a CEPIC seminar on Google. The Google image search scrapes images from their original sites and displays them in its own environment. This is bad for rightsholders as images can be saved and downloaded direct from Google without reference to the original site. Picture libraries and agencies lose significant traffic to their sites as a result with a German agencies survey indicating a drop of 50 percent in traffic. The recent fine levied by the EU on Google for anti-competitiveness in comparative shopping sites is encouraging and has paved the way for scrutiny of Google’s actions with online images.
The second presentation of the afternoon presented a solution for the problems raised in the Google seminar. SmartFrame technology allows images to be presented online without the danger of being scraped by Google as this is disabled by technical means. Most of the mechanisms people use to download images – like right-click – are disabled too. Images can be shared as links so social media sharing doesn’t lead to an image becoming orphaned and lost in the websphere. And when an image is viewed as a thumbnail in Google, there is a clear indication that it is a copyrighted image, and a link back to the originating site. Rob Sewel, Pixelrights CEO demonstrated how product items within an image could be linked back to a brand website, providing ways of funding photography in the future where photography provides a link to a paid-for advertising service. The technology could be put to all sorts of uses in both commercial and non-commercial fields, and gives control back to creators and their agents.
The success of this kind of technology, as with all solutions to image grabbing and orphaned images, lies in the uptake of the technology. To be truly protective of copyright, client websites would need to implement a technology like SmartFrame.
The IPTC Photo Metadata Conference 2017 was fascinating from start to finish for the about 60 attendees on location, the level of presentations was extremely high, and the presentations and videos are all available on the website at https://iptc.org/events/photo-metadata-conference-2017/.
Sarah Saunders runs Electric Lane, an independent DAM consultancy specialising in workflow planning, asset retrieval, data management and DAM project management. She works with IPTC’s Photo Metadata Working Group.